Can Endothelial Injury Provide the Passage to Explain the Vascular Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors?
- PMID: 27283526
- PMCID: PMC5508983
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308978
Can Endothelial Injury Provide the Passage to Explain the Vascular Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors?
Keywords: Editorial; endothelial dysfunction; proton pump inhibitors; vascular function.
Figures
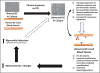
Comment on
-
Proton Pump Inhibitors Accelerate Endothelial Senescence.Circ Res. 2016 Jun 10;118(12):e36-42. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308807. Epub 2016 May 10. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27166251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forgacs I, Loganayagam A. Overprescribing proton pump inhibitors. BMJ. 2008;336:2–3. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39406.449456.BE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naunton M, Peterson GM, Bleasel MD. Overuse of proton pump inhibitors. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2000;25:333–340. - PubMed
-
- Fusaro M, Noale M, Tripepi G, Giannini S, D’Angelo A, Pica A, Calò LA, Miozzo D, Gallieni M. Long-term proton pump inhibitor use is associated with vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study using propensity score analysis. Drug Saf. 2013;36:635–642. doi: 10.1007/s40264-013-0062-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

