Synergy between histone deacetylase inhibitors and DNA-damaging agents is mediated by histone deacetylase 2 in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 27283986
- PMCID: PMC5190114
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9887
Synergy between histone deacetylase inhibitors and DNA-damaging agents is mediated by histone deacetylase 2 in colorectal cancer
Abstract
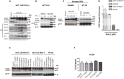
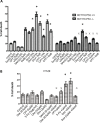
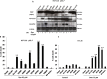
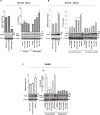
Previous studies have associated the overexpression of histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) and the presence of TP53 mutations with the progression to advanced stage drug resistant colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the mechanistic link between HDAC2 expression and the TP53 mutational status has remained unexplored. Here, we investigated the function of HDAC2 in drug resistance by assessing the synergistic effects of DNA-targeted chemotherapeutic agents and HDAC inhibitors (HDACis) on two TP53-mutated colorectal adenocarcinoma CRC cell lines (SW480 and HT-29) and on the TP53-wild type carcinoma cell line (HCT116 p53+/+) and its TP53 deficient sub-line (HCT116 p53-/-). We showed that in the untreated SW480 and HT-29 cells the steady-state level of HDAC2 was low compared to a TP53-wild type carcinoma cell line (HCT116 p53+/+). Increased expression of HDAC2 correlated with drug resistance, and depletion by shRNA sensitised the multi-drug resistance cell line HT-29 to CRC chemotherapeutic drugs such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and oxaliplatin (Oxa). Combined treatment with the HDACi suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid plus 5-FU or Oxa reduced the level of HDAC2 expression, modified chromatin structure and induced mitotic cell death in HT-29 cells. Non-invasive bioluminescence imaging revealed significant reductions in xenograft tumour growth with HDAC2 expression level reduced to <50% in treated animals. Elevated levels of histone acetylation on residues H3K9, H4K12 and H4K16 were also found to be associated with resistance to VPA/Dox or SAHA/Dox treatment. Our results suggest that HDAC2 expression rather than the p53 mutation status influences the outcome of combined treatment with a HDACi and DNA-damaging agents in CRC.
Keywords: HDAC2; colorectal cancer; drug resistance and in vivo imaging; histone acetylation; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of the HDAC inhibitor CG2 in combination with irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, or oxaliplatin on HCT116 colon cancer cells and xenografts.Oncol Rep. 2010 Dec;24(6):1509-14. doi: 10.3892/or_00001012. Oncol Rep. 2010. PMID: 21042746
-
HDAC2 deficiency and histone acetylation.Nat Genet. 2008 Jul;40(7):812-3; author reply 813. doi: 10.1038/ng0708-812. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18583969 No abstract available.
-
MSH3 mismatch repair protein regulates sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs and a histone deacetylase inhibitor in human colon carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e65369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065369. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724141 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 2 selective inhibitors: A versatile therapeutic strategy as next generation drug target in cancer therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Aug;170:105695. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105695. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34082029 Review.
-
Cancer cells' epigenetic composition and predisposition to histone deacetylase inhibitor sensitization.Epigenomics. 2011 Apr;3(2):145-55. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.12. Epigenomics. 2011. PMID: 21743813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors as cancer therapeutics.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Aug;4(15):287. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.07.22. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27568481 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of SNHG15 in the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Pers Med. 2022 May 6;12(5):753. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050753. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking Nature's Potential: Ferritin as a Universal Nanocarrier for Amplified Cancer Therapy Testing via 3D Microtissues.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Dec 25;16(51):70187-70204. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c12524. Epub 2024 Dec 11. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39660468 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 25;26(5):1988. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051988. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Approaches to Overcome Fluoropyrimidines Resistance in Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;14(3):695. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030695. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158962 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hajji N, Wallenborg K, Vlachos P, Fullgrabe J, Hermanson O, Joseph B. Opposing effects of hMOF and SIRT1 on H4K16 acetylation and the sensitivity to the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide. Oncogene. 2010;29:2192–204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

