Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Cervical Spinal Intramedullary Metastasis and Multiple Brain Metastases: A Case Report
- PMID: 27284497
- PMCID: PMC4889451
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.590
Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Cervical Spinal Intramedullary Metastasis and Multiple Brain Metastases: A Case Report
Abstract
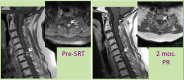
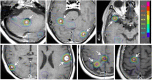
A case of cervical (C) spinal intramedullary metastasis and multiple small brain metastases from papillary thyroid carcinoma was presented. Spinal metastasis caused posterior neck and left shoulder pain, dysesthesia in both legs, and motor weakness in both legs and left arm, though the brain metastases were asymptomatic. Both the spinal and brain metastases were successfully treated by frameless stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT)/stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). The patient's symptoms were almost entirely relieved within two months. A 76-year-old woman was diagnosed as having a thyroid tumor and lung metastasis by roentgenography and computed tomography. Biopsy of the thyroid tumor extending into the mediastinum revealed papillary thyroid carcinoma. She underwent surgical resection of thyroid with dissection of the mediastinum lymph node area. Internal oral radioisotope therapy was not effective for the multiple small lung metastases. She did well for 15 months, but later developed posterior neck and left shoulder pain and dysesthesia in the right leg and then dysesthesia and motor weakness in both legs. Then she experienced weakness in the left upper extremity. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) disclosed a small cervical spinal intramedullary mass lesion at the level of C6 and C7 on the left side as well as nine small brain lesions. The cervical spinal intramedullary metastatic tumor was treated by volumetric modulated arc radiotherapy (VMAT) SRT and the nine small brain metastatic tumors were treated by dynamic conformal arc (DCA) SRS uneventfully. A total dose of 39 Gy (100% dose) was delivered in 13 fractions for the spinal lesion (prescription, D95=95% dose; maximum dose=46.3 Gy). Single fraction SRS of 22 Gy (prescription, D95=100% dose) was performed for each of the nine small brain tumors. The spinal tumor was decreased in size on follow-up MRI two months after SRT. Three of the nine brain lesions had disappeared and six were decreased in size on follow-up MRI two months after SRS. Motor weakness in the left extremities and right leg was fully improved, and she could walk again without a cane within two months after SRT. She had only slight dysesthesia in the right leg, possibly due to lumbar spondylosis at the end of the six-month follow-up after SRT. The spinal tumor continued to decrease in size on follow-up MRI five months after SRT. Eight of the nine brain lesions had disappeared and one was decreased in size on follow-up MRI five months after SRS.
Keywords: Stereotactic Radiosurgery; brain metastasis; dynamic conformal arc therapy; intramedullary spinal cord metastases; papillary thyroid carcinoma; simultaneous integrated boost; spine metastasis; stereotactic radiotherapy; true beam s tx; volumetric modulated arc therapy (vmat).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, Sato Y, Jokura H, Yomo S, Nagano O, Kenai H, Moriki A, Suzuki S, Kida Y, Iwai Y, Hayashi M, Onishi H, Gondo M, Sato M, Akimitsu T, Kubo K, Kikuchi Y, Shibasaki T, Goto T, Takanashi M, Mori Y, Takakura K, Saeki N, Kunieda E, Aoyama H, Momoshima S, Tsuchiya K. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:387–395. - PubMed
-
- Stereotactic spine radiosurgery for intradural and intramedullary metastasis. Shin DA, Huh R, Chung SS, Rock J, Ryu S. Neurosurg Focus. 2009;27:10. - PubMed
-
- Fractionated radiosurgical management of intramedullary spinal cord metastasis: a case report and review of the literature. Parikh S, Heron DE. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009;111:858–861. - PubMed
-
- Stereotactic radiotherapy for spinal intradural metastases developing within or adjacent to the previous irradiation field. Report of three cases. Mori Y, Hashizume C, Shibamoto Y, Kobayashi T, Nakazawa H, Hagiwara M, Tsugawa T. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4345672/ Nagoya J Med Sci. 2013;75:263–271. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis treated with radiation therapy: report of 3 cases. Endo S, Hida K, Yano S, Ito M, Yamaguchi S, Kashiwazaki D, Kinoshita R, Shirato H, Iwasaki Y. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/18411800. No Shinkei Geka. 2008;36:345–349. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
