Axin-1 Regulates Meiotic Spindle Organization in Mouse Oocytes
- PMID: 27284927
- PMCID: PMC4902301
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157197
Axin-1 Regulates Meiotic Spindle Organization in Mouse Oocytes
Abstract
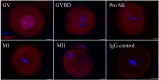
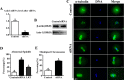
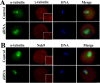
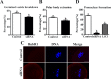
Axin-1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a versatile scaffold protein involved in centrosome separation and spindle assembly in mitosis, but its function in mammalian oogenesis remains unknown. Here we examined the localization and function of Axin-1 during meiotic maturation in mouse oocytes. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that Axin-1 was localized around the spindle. Knockdown of the Axin1 gene by microinjection of specific short interfering (si)RNA into the oocyte cytoplasm resulted in severely defective spindles, misaligned chromosomes, failure of first polar body (PB1) extrusion, and impaired pronuclear formation. However, supplementing the culture medium with the Wnt pathway activator LiCl improved spindle morphology and pronuclear formation. Downregulation of Axin1 gene expression also impaired the spindle pole localization of γ-tubulin/Nek9 and resulted in retention of the spindle assembly checkpoint protein BubR1 at kinetochores after 8.5 h of culture. Our results suggest that Axin-1 is critical for spindle organization and cell cycle progression during meiotic maturation in mouse oocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Manandhar G, Schatten H, Sutovsky P. Centrosome reduction during gametogenesis and its significance. Biology of reproduction. 2005;72:2–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

