The use of CrossMAb technology for the generation of bi- and multispecific antibodies
- PMID: 27285945
- PMCID: PMC4968094
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1197457
The use of CrossMAb technology for the generation of bi- and multispecific antibodies
Erratum in
-
Correction.MAbs. 2019 Jan;11(1):217. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1546991. Epub 2018 Nov 13. MAbs. 2019. PMID: 30422058 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
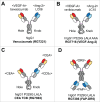
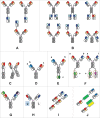
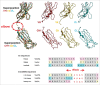
The major challenge in the generation of bispecific IgG antibodies is enforcement of the correct heavy and light chain association. The correct association of generic light chains can be enabled using immunoglobulin domain crossover, known as CrossMAb technology, which can be combined with approaches enabling correct heavy chain association such as knobs-into-holes (KiH) technology or electrostatic steering. Since its development, this technology has proven to be very versatile, allowing the generation of various bispecific antibody formats, not only heterodimeric/asymmetric bivalent 1+1 CrossMAbs, but also tri- (2+1), tetravalent (2+2) bispecific and multispecific antibodies. Numerous CrossMAbs have been evaluated in preclinical studies, and, so far, 4 different tailor-made bispecific antibodies based on the CrossMAb technology have entered clinical studies. Here, we review the properties and activities of bispecific CrossMAbs and give an overview of the variety of CrossMAb-enabled antibody formats that differ from heterodimeric 1+1 bispecific IgG antibodies.
Keywords: 2+1, 1+1; 2+2; Ang-2; CEA TCB; CrossMAb; DAF-CrossMAb; DVD-CrossMAb; DuoMAb; EGFR; HER1; HER3; Immunoglobulin domain crossover; Kappa-Lambda-CrossMAb; MoAb; MoAb-Dimer; MonoMAb; P329G LALA; RG7221; RG7386; RG7716; RG7802; Triple A; VEGF-A; asymmetric; heterodimeric; knobs-into-holes (KiH); vanucizumab.
Figures

References
-
- Schaefer W, Volger HR, Lorenz S, Imhof-Jung S, Regula JT, Klein C, Molhoj M. Heavy and light chain pairing of bivalent quadroma and knobs-into-holes antibodies analyzed by uhr-esi-qtof mass spectrometry. MAbs 2016; 8(1):49-55; PMID:26496506; http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2015.1111498 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klein C, Sustmann C, Thomas M, Stubenrauch K, Croasdale R, Schanzer J, Brinkmann U, Kettenberger H, Regula JT, Schaefer W. Progress in overcoming the chain association issue in bispecific heterodimeric igg antibodies. MAbs 2012; 4(6):653-63; PMID:22925968; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/mabs.21379 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Merchant AM, Zhu Z, Yuan JQ, Goddard A, Adams CW, Presta LG, Carter P. An efficient route to human bispecific igg. Nat Biotechnol 1998; 16(7):677-81; PMID:9661204; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nbt0798-677 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schaefer W, Regula JT, Bahner M, Schanzer J, Croasdale R, Durr H, Gassner C, Georges G, Kettenberger H, Imhof-Jung S, et al.. Immunoglobulin domain crossover as a generic approach for the production of bispecific igg antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108(27):11187-92; PMID:21690412; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1019002108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dengl S, Wehmer M, Hesse F, Lipsmeier F, Popp O, Lang K. Aggregation and chemical modification of monoclonal antibodies under upstream processing conditions. Pharm Res 2013; 30(5):1380-99; PMID:23322133; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-0977-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
