TMPRSS2-ERG fusion protein regulates insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) gene expression in prostate cancer: involvement of transcription factor Sp1
- PMID: 27285981
- PMCID: PMC5239482
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9837
TMPRSS2-ERG fusion protein regulates insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) gene expression in prostate cancer: involvement of transcription factor Sp1
Abstract
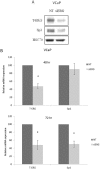
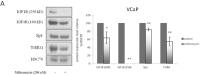
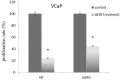
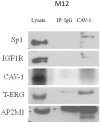
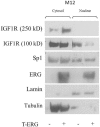
Prostate cancer is a major health issue in the Western world. The most common gene rearrangement in prostate cancer is the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, which results in aberrant expression of the transcription factor ERG. The insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) plays a key role in cell growth and tumorigenesis, and is overexpressed in most malignancies, including prostate cancer. In this study we show that TMPRSS2-ERG mediates its tumorigenic effects through regulation of IGF1R gene expression. Silencing of T-ERG in VCaP cells resulted in downregulation of both IGF1R and Sp1, a critical IGF1R regulator. Co-immunoprecipitation assays revealed a physical interaction between transcription factors ERG and Sp1, with potential relevance in IGF1R gene regulation. In addition, transactivation of the IGF1R gene by ERG was mediated at the level of transcription, as indicated by results of promoter assays. To identify new co-activators of the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion protein we performed mass spectrometry-based proteomic analyses. Among other interactors, we identified AP-2 complex subunit mu (AP2M1) and caveolin-1 (CAV1) in association with ERG in cell nuclei. These proteins play a mechanistic role in IGF1R internalization. Our analyses are consistent with a potential novel function of TMPRSS2-ERG as a major regulator of IGF1R gene expression. Results may impinge upon ongoing efforts to target the IGF1R in the clinics.
Keywords: IGF1 receptor; TMPRSS2-ERG; fusion proteins; insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1); prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no Conflicts of Interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Significance of the TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):5450-5458. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7281. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849022 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of IGF/insulin receptor in prostate cancer tissue and progression to lethal disease.Carcinogenesis. 2018 Dec 31;39(12):1431-1437. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy112. Carcinogenesis. 2018. PMID: 30165429 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genetic interaction between Tmprss2-ERG gene fusion and Nkx3.1-loss does not enhance prostate tumorigenesis in mouse models.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0120628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120628. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25780911 Free PMC article.
-
ERG protein expression as a biomarker of prostate cancer.Biomark Med. 2013 Dec;7(6):851-65. doi: 10.2217/bmm.13.105. Biomark Med. 2013. PMID: 24266818 Review.
-
[The progress of TMPRSS2-ETS gene fusions and their mechanism in prostate cancer].Yi Chuan. 2011 Feb;33(2):117-22. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.00117. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 21377967 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Decoding Oncofusions: Unveiling Mechanisms, Clinical Impact, and Prospects for Personalized Cancer Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;15(14):3678. doi: 10.3390/cancers15143678. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic fusion proteins adopt the insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0807-z. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor affects the survival of primary prostate cancer patients depending on TMPRSS2-ERG status.BMC Cancer. 2017 May 25;17(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3356-8. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28545426 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Pathway Targeting in Cancer: Role of the IGF Axis and Opportunities for Future Combination Studies.Target Oncol. 2017 Oct;12(5):571-597. doi: 10.1007/s11523-017-0514-5. Target Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28815409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FusionAI: Predicting fusion breakpoint from DNA sequence with deep learning.iScience. 2021 Sep 25;24(10):103164. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103164. eCollection 2021 Oct 22. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34646994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D, Brodt P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocrine reviews. 2007;28:20–47. - PubMed
-
- Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A, Friend KE. The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocrine reviews. 2000;21:215–244. - PubMed
-
- Werner H, Maor S. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene: a downstream target for oncogene and tumor suppressor action. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism. 2006;17:236–242. - PubMed
-
- DiGiovanni J, Kiguchi K, Frijhoff A, Wilker E, Bol DK, Beltran L, Moats S, Ramirez A, Jorcano J, Conti C. Deregulated expression of insulin-like growth factor I in prostate epithelium leads to neoplasia in transgenic mice. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences USA. 2000;97:3455–3460. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH, Pollak M. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science. 1998;279:563–566. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

