MicroRNA-20a-5p promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by downregulating Smad4
- PMID: 27286257
- PMCID: PMC5216716
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9900
MicroRNA-20a-5p promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by downregulating Smad4
Abstract
Background: Tumor metastasis is one of the leading causes of poor prognosis for colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. Loss of Smad4 contributes to aggression process in many human cancers. However, the underlying precise mechanism of aberrant Smad4 expression in CRC development is still little known.
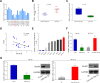
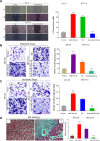
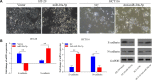
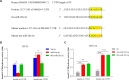
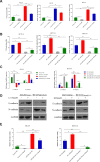
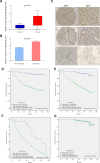
Results: miR-20a-5p negatively regulated Smad4 by directly targeting its 3'UTR in human colorectal cancer cells. miR-20a-5p not only promoted CRC cells aggression capacity in vitro and liver metastasis in vivo, but also promoted the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition process by downregulating Smad4 expression. In addition, tissue microarray analysis obtained from 544 CRC patients' clinical characters showed that miR-20a-5p was upregulated in human CRC tissues, especially in the tissues with metastasis. High level of miR-20a-5p predicted poor prognosis in CRC patients.
Methods: Five miRNA target prediction programs were applied to identify potential miRNA(s) that target(s) Smad4 in CRC. Luciferase reporter assay and transfection technique were used to validate the correlation between miR-20a-5p and Smad4 in CRC. Wound healing, transwell and tumorigenesis assays were used to explore the function of miR-20a-5p and Smad4 in CRC progression in vitro and in vivo. The association between miR-20a-5p expression and the prognosis of CRC patients was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier analysis and multivariate cox proportional hazard analyses based on tissue microarray data.
Conclusions: miR-20a-5p, as an onco-miRNA, promoted the invasion and metastasis ability by suppressing Smad4 expression in CRC cells, and high miR-20a-5p predicted poor prognosis for CRC patients, providing a novel and promising therapeutic target in human colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Smad4; colorectal cancer; metastasis; miR-20a-5p; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GDPD5, a target of miR-195-5p, is associated with metastasis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:945-952. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29635904
-
miR-196a-5p promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via targeting IκBα.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jan 8;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5245-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30621631 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑20a is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer and is involved in cell metastasis.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jul;10(1):283-91. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2144. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24737193
-
Oncogenic miRNAs and target therapies in colorectal cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Sep;508:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 11. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32407782 Review.
-
The Efficacy of miR-20a as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 3;11(8):1111. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081111. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31382594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The microRNA-210-Stathmin1 Axis Decreases Cell Stiffness to Facilitate the Invasiveness of Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 12;13(8):1833. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081833. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921319 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Study on the Anti-cancer Effects of Quercetin and Its Epigenetic Modifications in Arresting Progression of Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023 Feb 20;71(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00005-023-00669-w. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023. PMID: 36807774 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of IRS-1, RUNX3 and SMAD4 Are Positive Prognostic Factors in Stage I-III Colon Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;15(5):1448. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051448. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900240 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal cancer and therapy response: a focus on the main mechanisms involved.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 19;13:1208140. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1208140. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37538108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling the Immune Suppressor: Transcription Factors and MicroRNAs Regulating CD73/NT5E.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 18;9:813. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00813. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29720980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

