A Comprehensive Review of Treprostinil Pharmacokinetics via Four Routes of Administration
- PMID: 27286723
- PMCID: PMC5107196
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-016-0409-0
A Comprehensive Review of Treprostinil Pharmacokinetics via Four Routes of Administration
Abstract
Treprostinil is available in three different formulations and four different routes of administration: Remodulin® (treprostinil sodium, intravenous and subcutaneous administration), Tyvaso® (treprostinil sodium, inhaled administration), and Orenitram® (treprostinil diolamine, oral administration) for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in healthy volunteers and patients with PAH. The intent of this review is to outline pharmacokinetic considerations of the three treprostinil formulations and provide clinicians with a resource that may support clinical decisions in treating patients with PAH.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical StandardsFundingNo external funds were used in the preparation of this manuscript.Conflicts of interestParag Kumar and Emily Thudium completed post-doctoral fellowships with United Therapeutics and Parag Kumar is currently employed by the National Institutes of Health. Kevin Laliberte, David Zaccardelli, and Andrew Nelsen are employees of United Therapeutics Corp.
Figures

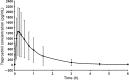

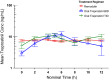
References
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(17):1573–1619. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patel J, Shen L, Hall S, et al. EP2 receptors play a key role in mediating the anti-proliferative activity of treprostinil in smooth muscle cells derived from the lungs of pulmonary hypertensive patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191:A5954.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

