Differential transcriptional regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by arsenite under normoxia and hypoxia: involvement of Nrf2
- PMID: 27286880
- PMCID: PMC5052318
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-016-1439-7
Differential transcriptional regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by arsenite under normoxia and hypoxia: involvement of Nrf2
Abstract
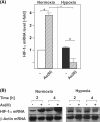
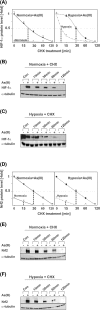
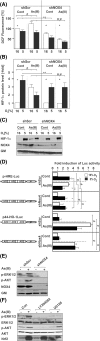
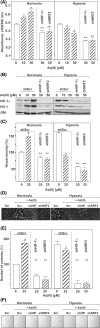
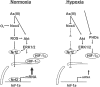
Arsenite (As(III)) is widely distributed in nature and can be found in water, food, and air. There is significant evidence that exposure to As(III) is associated with human cancers originated from liver, lung, skin, bladder, kidney, and prostate. Hypoxia plays a role in tumor growth and aggressiveness; adaptation to it is, at least to a large extent, mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). In the current study, we investigated As(III) effects on HIF-1α under normoxia and hypoxia in the hepatoma cell line HepG2. We found that As(III) increased HIF-1α protein levels under normoxia while the hypoxia-mediated induction of HIF1α was reduced. Thereby, the As(III) effects on HIF-1α were dependent on both, transcriptional regulation via the transcription factor Nrf2 mediated by NOX4, PI3K/Akt, and ERK1/2 as well as by modulation of HIF-1α protein stability. In line, the different effects of As(III) via participation of HIF-1α and Nrf2 were also seen in tube formation assays with endothelial cells where knockdown of Nrf2 and HIF-1α abolished As(III) effects. Overall, the present study shows that As(III) is a potent inducer of HIF-1α under normoxia but not under hypoxia which may explain, in part, its carcinogenic as well as anti-carcinogenic actions.
Key message: As(III) increased HIF-1α under normoxia but reduced its hypoxia-dependent induction. The As(III) effects on HIF-1α were dependent on ROS, NOX4, PI3K/Akt, and ERK1/2. The As(III) effects under normoxia involved transcriptional regulation via Nrf2. Knockdown of Nrf2 and HIF-1α abolished As(III) effects in tube formation assays. The data may partially explain As(III)'s carcinogenic and anti-carcinogenic actions.
Keywords: Arsenite As(III); Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1α); Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); NADPH enzyme oxidase 4 (NOX4); Reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) modulation in heavy metal toxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2023 May;97(5):1299-1318. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03483-7. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36933023 Review.
-
Arsenite induces HIF-1alpha and VEGF through PI3K, Akt and reactive oxygen species in DU145 human prostate carcinoma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Jan;255(1-2):33-45. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000007259.65742.16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 14971644
-
Transcriptional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by insulin-like growth factor-1 via MAP kinases and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in HepG2 cells.Thromb Haemost. 2005 Jun;93(6):1176-84. doi: 10.1160/TH04-11-0761. Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 15968405
-
Andrographolide inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-driven endothelin 1 secretion by activating Nrf2/HO-1 and promoting the expression of prolyl hydroxylases 2/3 in human endothelial cells.Environ Toxicol. 2017 Mar;32(3):918-930. doi: 10.1002/tox.22293. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Environ Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27297870
-
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: new developments in an old debate.J Cell Biochem. 2015 May;116(5):696-703. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25074. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25546605 Review.
Cited by
-
hZIP1 Inhibits Progression of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing NF-kB/HIF-1α Pathway.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 2;11:759818. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.759818. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34926261 Free PMC article.
-
The epigenetic landscape related to reactive oxygen species formation in the cardiovascular system.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;174(12):1533-1554. doi: 10.1111/bph.13792. Epub 2017 May 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28332701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and Hypoxia: Points of Interplay in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;14(7):1791. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071791. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) modulation in heavy metal toxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2023 May;97(5):1299-1318. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03483-7. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36933023 Review.
-
NF-κB1 p50 stabilizes HIF-1α protein through suppression of ATG7-dependent autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Dec 27;13(12):1076. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05521-1. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36575197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The World Bank . Towards a more effective operational response. Washington, DC: The World Bank; 2005.
-
- Arsenic and arsenic compounds (1980). IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risk Chem Hum 23:39-141 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

