Dual NAMPT and BTK Targeting Leads to Synergistic Killing of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Cells Regardless of MYD88 and CXCR4 Somatic Mutation Status
- PMID: 27287071
- PMCID: PMC5771267
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0630
Dual NAMPT and BTK Targeting Leads to Synergistic Killing of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Cells Regardless of MYD88 and CXCR4 Somatic Mutation Status
Abstract
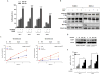
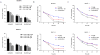
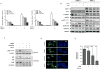
Purpose: Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt) regulates intracellular NAD+ pool and is highly expressed in a number of malignancies. FK866, a selective inhibitor of Nampt, depletes intracellular NAD+ levels, thereby blocking cellular metabolism and triggering sensitization to other drugs and cell death. Here we characterized the antitumor effects of Nampt inhibition in Waldenström macroglobulinemia.
Experimental design: We investigated Nampt role in MW cells using both mRNA and protein expression analyses. We have also used loss-of-function approaches to investigate the growth and survival effects of Nampt on MW cells and further tested the anti-MW activity of dual Nampt and BTK inhibition in vitro and in vivo RESULTS: We found that Waldenström macroglobulinemia cells exhibit high levels of Nampt compared with normal B cells. Loss of function studies suggested a potential oncogenic role of Nampt in Waldenström macroglobulinemia cells, and BTK-inhibitor ibrutinib and FK866 resulted in a significant and synergistic anti-Waldenström macroglobulinemia cell death, regardless of MYD88 and CXCR4 mutational status. Cell death was associated with: (i) activation of caspase-3, PARP and downregulation of Mcl-1, (ii) enhanced intracellular ATP and NAD+ depletion, (iii) inhibition of NF-κB signaling, and (iv) inhibition of multiple prosurvival signaling pathways. In a murine xenograft Waldenström macroglobulinemia model, low-dose combination FK866 and ibrutinib is well tolerated, significantly inhibits tumor growth, and prolongs host survival.
Conclusions: Our results show intracellular NAD+ level as crucial for proliferation and survival of Waldenström macroglobulinemia cells, and provides the mechanistic preclinical rationale for targeting Nampt, either alone or with Ibrutinib, to overcome drug resistance and improve patient outcome in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Clin Cancer Res; 22(24); 6099-109. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A mutation in MYD88 (L265P) supports the survival of lymphoplasmacytic cells by activation of Bruton tyrosine kinase in Waldenström macroglobulinemia.Blood. 2013 Aug 15;122(7):1222-32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-12-475111. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23836557
-
Intracellular NAD⁺ depletion enhances bortezomib-induced anti-myeloma activity.Blood. 2013 Aug 15;122(7):1243-55. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-483511. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23823317 Free PMC article.
-
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia cells devoid of BTKC481S or CXCR4WHIM-like mutations acquire resistance to ibrutinib through upregulation of Bcl-2 and AKT resulting in vulnerability towards venetoclax or MK2206 treatment.Blood Cancer J. 2017 May 26;7(5):e565. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2017.40. Blood Cancer J. 2017. PMID: 28548645 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics, Signaling, and Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar 20;35(9):994-1001. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.0814. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28294689 Review.
-
Zanubrutinib for the treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia.Expert Rev Hematol. 2020 Dec;13(12):1303-1310. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2020.1851184. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Expert Rev Hematol. 2020. PMID: 33297772 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of various NAMPT inhibitors for the treatment of cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 7;13:970553. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.970553. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD38-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction Primes Multiple Myeloma Cells for NAD+-Lowering Agents.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 15;12(2):494. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020494. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830052 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase prompts bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by driving macrophage M2 polarization in mice.Theranostics. 2024 Apr 28;14(7):2794-2815. doi: 10.7150/thno.94482. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38773984 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Energy Metabolism: Exploiting the Additional Roles of NAMPT for Cancer Therapy.Front Oncol. 2020 Jan 17;9:1514. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01514. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32010616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of CXCR4 by the Naturally Occurring CXCR4 Antagonist EPI-X4 in Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 16;13(4):826. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040826. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger F, Ramirez-Hernandez MH, Ziegler M. The new life of a centenarian: signalling functions of NAD(P) Trends in biochemical sciences. 2004;29:111–8. - PubMed
-
- Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nature reviews Cancer. 2011;11:85–95. - PubMed
-
- Chiarugi A, Dolle C, Felici R, Ziegler M. The NAD metabolome--a key determinant of cancer cell biology. Nature reviews Cancer. 2012;12:741–52. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

