Oncostatin M promotes excitotoxicity by inhibiting glutamate uptake in astrocytes: implications in HIV-associated neurotoxicity
- PMID: 27287400
- PMCID: PMC4903004
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0613-8
Oncostatin M promotes excitotoxicity by inhibiting glutamate uptake in astrocytes: implications in HIV-associated neurotoxicity
Abstract
Background: Elevated levels of oncostatin M (OSM), an interleukin-6 cytokine family member, have been observed in HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) and Alzheimer's disease. However, the function of OSM in these disease conditions is unclear. Since deficient glutamate uptake by astrocytes is instrumental in HAND-associated neurotoxicity, we hypothesized that OSM impairs glutamate uptake in astrocytes and thereby promotes neuronal excitotoxicity.
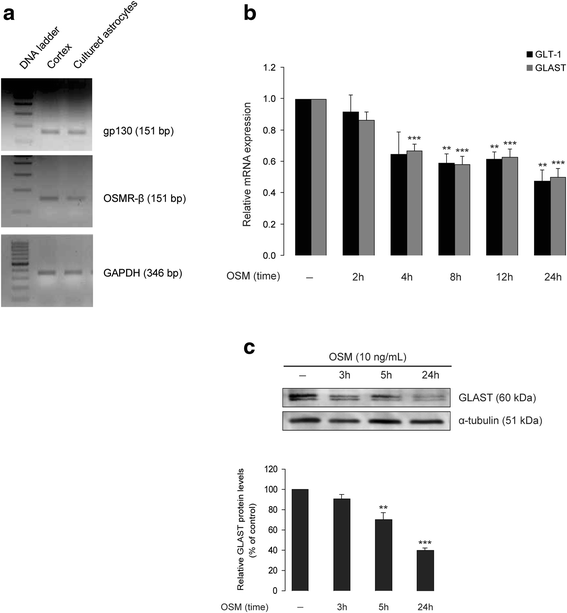
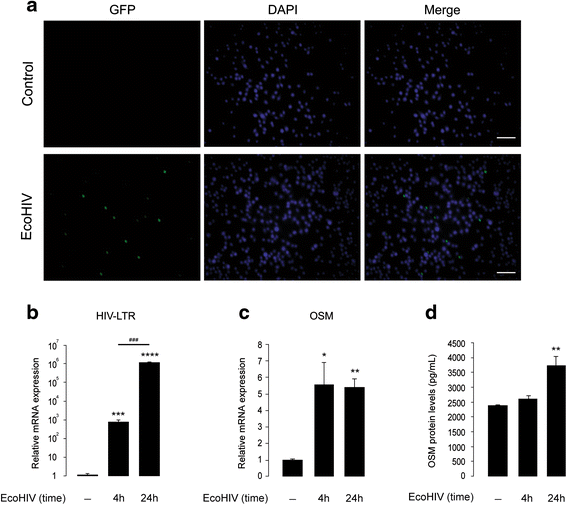
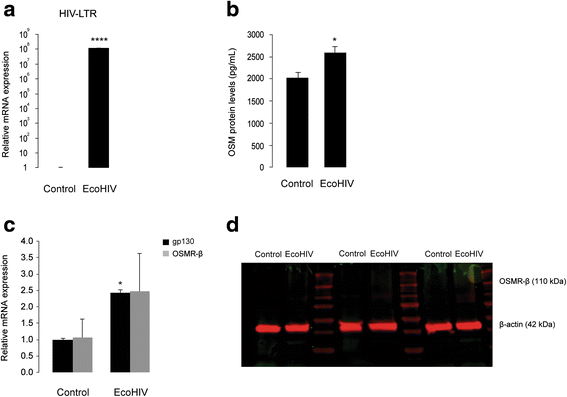
Methods: Primary cultures of mouse cortical astrocytes, neurons, microglia, and BV2 cell line were used. The expression of glutamate transporters (GLAST/EAAT1 and GLT-1/EAAT2) was investigated using real-time PCR and Western blot, and their activity was assessed by measuring (3)H-D-aspartate uptake. Neuronal toxicity was measured using the colorimetric MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl-) 2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay and immunocytochemistry. A chimeric HIV-1 that infects murine cells (EcoHIV/NL4-3-GFP virus (EcoHIV)) was used to investigate whether the virus induces OSM, OSM receptor (OSMR)-β, glycoprotein 130 (gp130), GLT-1, GLAST (mRNA and protein), and OSM release (ELISA) in cultured BV2 cells, primary microglia, or astrocytes. Statistical analyses of the data were performed using one-way ANOVA (to allow multiple comparisons) and two-tailed Student's t test.
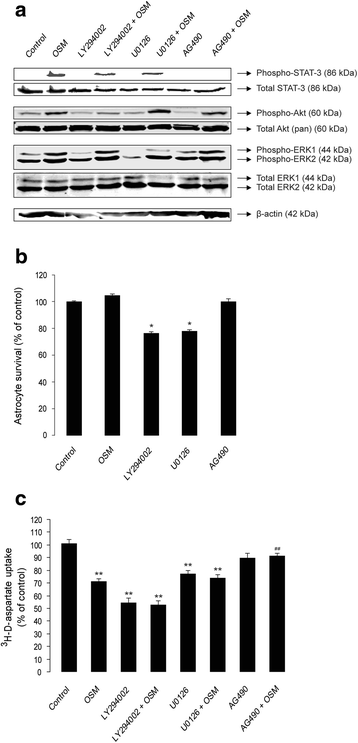
Results: OSM treatment (10 ng/mL) time-dependently reduced GLAST and GLT-1 expression and inhibited (3)H-D-aspartate uptake in cultured astrocytes in a concentration-dependent manner, an effect prevented by the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT)3 inhibitor AG490. Down-regulation of astrocytic glutamate transport by OSM resulted in NMDA receptor-dependent excitotoxicity in cortical neurons. Infection with EcoHIV induced OSM gene expression and protein release in BV2 cells and microglia, but not in astrocytes. Conversely, EcoHIV caused a fivefold increase in OSMR-β mRNA (but not gp130) and protein in astrocytes, but not in microglia, which did not express OSMR-β protein. Finally, astrocytic expression of GLAST gene was unaffected by EcoHIV, whereas GLT-1 mRNA was increased by twofold.
Conclusions: We provide first evidence that activation of JAK/STAT3 signaling by OSM inhibits glutamate uptake in astrocytes, which results in neuronal excitotoxicity. Our findings with EcoHIV suggest that targeting OSMR-β signaling in astrocytes might alleviate HIV-1-associated excitotoxicity.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Excitotoxicity; GLAST; GLT-1; Glutamate; HIV; Interleukin 6; NMDA; Oncostatin M.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of astrocytic glutamate transporter expression by Akt: evidence for a selective transcriptional effect on the GLT-1/EAAT2 subtype.J Neurochem. 2006 May;97(3):759-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03743.x. Epub 2006 Mar 29. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16573655
-
Amyloid-beta peptide decreases glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes: involvement of oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades.Neuroscience. 2008 Oct 28;156(4):898-910. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.08.022. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18790019
-
Regulation of glutamate transporter GLAST and GLT-1 expression in astrocytes by estrogen.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005 Jul 29;138(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.10.043. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15896872
-
The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Dec 15;161:107559. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30851309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1, methamphetamine and astrocyte glutamate regulation: combined excitotoxic implications for neuro-AIDS.Curr HIV Res. 2012 Jul;10(5):392-406. doi: 10.2174/157016212802138832. Curr HIV Res. 2012. PMID: 22591363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIV Nef Expression Down-modulated GFAP Expression and Altered Glutamate Uptake and Release and Proliferation in Astrocytes.Aging Dis. 2023 Feb 1;14(1):152-169. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0712. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 36818564 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical relevance of OSM in inflammatory diseases: a comprehensive review.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 29;14:1239732. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239732. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37841259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of Immune Activation in HIV and Non HIV Subjects and Its Relation to Cardiovascular Disease Risk.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 5;12:647805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.647805. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34290695 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling in Activated Astrocytes Drives Network Hyperexcitability in Aβ-Bearing Mice.J Neurosci. 2017 Jun 21;37(25):6132-6148. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0877-17.2017. Epub 2017 May 30. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28559377 Free PMC article.
-
Oncostatin M, an Underestimated Player in the Central Nervous System.Front Immunol. 2019 May 29;10:1165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01165. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31191538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

