Airway Memory CD4(+) T Cells Mediate Protective Immunity against Emerging Respiratory Coronaviruses
- PMID: 27287409
- PMCID: PMC4917442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.05.006
Airway Memory CD4(+) T Cells Mediate Protective Immunity against Emerging Respiratory Coronaviruses
Abstract
Two zoonotic coronaviruses (CoVs)-SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV-have crossed species to cause severe human respiratory disease. Here, we showed that induction of airway memory CD4(+) T cells specific for a conserved epitope shared by SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV is a potential strategy for developing pan-coronavirus vaccines. Airway memory CD4(+) T cells differed phenotypically and functionally from lung-derived cells and were crucial for protection against both CoVs in mice. Protection was dependent on interferon-γ and required early induction of robust innate and virus-specific CD8(+) T cell responses. The conserved epitope was also recognized in SARS-CoV- and MERS-CoV-infected human leukocyte antigen DR2 and DR3 transgenic mice, indicating potential relevance in human populations. Additionally, this epitope was cross-protective between human and bat CoVs, the progenitors for many human CoVs. Vaccine strategies that induce airway memory CD4(+) T cells targeting conserved epitopes might have broad applicability in the context of new CoVs and other respiratory virus outbreaks.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
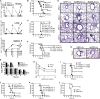

References
-
- Agnihothram S., Gopal R., Yount B.L., Jr., Donaldson E.F., Menachery V.D., Graham R.L., Scobey T.D., Gralinski L.E., Denison M.R., Zambon M., Baric R.S. Evaluation of serologic and antigenic relationships between middle eastern respiratory syndrome coronavirus and other coronaviruses to develop vaccine platforms for the rapid response to emerging coronaviruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2014;209:995–1006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolles M., Deming D., Long K., Agnihothram S., Whitmore A., Ferris M., Funkhouser W., Gralinski L., Totura A., Heise M., Baric R.S. A double-inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus vaccine provides incomplete protection in mice and induces increased eosinophilic proinflammatory pulmonary response upon challenge. J. Virol. 2011;85:12201–12215. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese SARS Molecular Epidemiology Consortium Molecular evolution of the SARS coronavirus during the course of the SARS epidemic in China. Science. 2004;303:1666–1669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

