Pexmetinib: A Novel Dual Inhibitor of Tie2 and p38 MAPK with Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 27287719
- PMCID: PMC5398415
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3062
Pexmetinib: A Novel Dual Inhibitor of Tie2 and p38 MAPK with Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
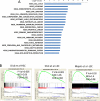
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) suppress normal hematopoietic activity in part by enabling a pathogenic inflammatory milieu in the bone marrow. In this report, we show that elevation of angiopoietin-1 in myelodysplastic CD34(+) stem-like cells is associated with higher risk disease and reduced overall survival in MDS and AML patients. Increased angiopoietin-1 expression was associated with a transcriptomic signature similar to known MDS/AML stem-like cell profiles. In seeking a small-molecule inhibitor of this pathway, we discovered and validated pexmetinib (ARRY-614), an inhibitor of the angiopoietin-1 receptor Tie-2, which was also found to inhibit the proinflammatory kinase p38 MAPK (which is overactivated in MDS). Pexmetinib inhibited leukemic proliferation, prevented activation of downstream effector kinases, and abrogated the effects of TNFα on healthy hematopoietic stem cells. Notably, treatment of primary MDS specimens with this compound stimulated hematopoiesis. Our results provide preclinical proof of concept for pexmetinib as a Tie-2/p38 MAPK dual inhibitor applicable to the treatment of MDS/AML. Cancer Res; 76(16); 4841-9. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

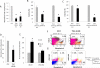



References
-
- Verma A, List A. Cytokine targets in Myelodysplastic syndromes. Curr Hematol Rep. 2005 In Print. - PubMed
-
- Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M, Sato H, Matsuoka S, Takubo K, et al. Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell. 2004;118:149–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

