The novel enterochromaffin marker Lmx1a regulates serotonin biosynthesis in enteroendocrine cell lineages downstream of Nkx2.2
- PMID: 27287799
- PMCID: PMC4958331
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.130682
The novel enterochromaffin marker Lmx1a regulates serotonin biosynthesis in enteroendocrine cell lineages downstream of Nkx2.2
Abstract
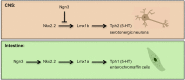
Intestinal hormone-producing cells represent the largest endocrine system in the body, but remarkably little is known about enteroendocrine cell type specification in the embryo and adult. We analyzed stage- and cell type-specific deletions of Nkx2.2 and its functional domains in order to characterize its role in the development and maintenance of enteroendocrine cell lineages in the mouse duodenum and colon. Although Nkx2.2 regulates enteroendocrine cell specification in the duodenum at all stages examined, it controls the differentiation of progressively fewer enteroendocrine cell populations when deleted from Ngn3(+) progenitor cells or in the adult duodenum. During embryonic development Nkx2.2 regulates all enteroendocrine cell types, except gastrin and preproglucagon. In developing Ngn3(+) enteroendocrine progenitor cells, Nkx2.2 is not required for the specification of neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, indicating that a subset of these cell populations derive from an Nkx2.2-independent lineage. In adult duodenum, Nkx2.2 becomes dispensable for cholecystokinin and secretin production. In all stages and Nkx2.2 mutant conditions, serotonin-producing enterochromaffin cells were the most severely reduced enteroendocrine lineage in the duodenum and colon. We determined that the transcription factor Lmx1a is expressed in enterochromaffin cells and functions downstream of Nkx2.2. Lmx1a-deficient mice have reduced expression of Tph1, the rate-limiting enzyme for serotonin biosynthesis. These data clarify the function of Nkx2.2 in the specification and homeostatic maintenance of enteroendocrine populations, and identify Lmx1a as a novel enterochromaffin cell marker that is also essential for the production of the serotonin biosynthetic enzyme Tph1.
Keywords: Enterochromaffin; Enteroendocrine cells; Intestine; Lmx1a; Nkx2.2; Serotonin.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rfx6 promotes the differentiation of peptide-secreting enteroendocrine cells while repressing genetic programs controlling serotonin production.Mol Metab. 2019 Nov;29:24-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.08.007. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31668390 Free PMC article.
-
The homeodomain-containing transcription factors Arx and Pax4 control enteroendocrine subtype specification in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036449. Epub 2012 May 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22570716 Free PMC article.
-
Nkx2.2 is expressed in a subset of enteroendocrine cells with expanded lineage potential.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Dec 15;309(12):G975-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00244.2015. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26492922 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of enterochromaffin cells within the gastrointestinal tract.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Jun;29(6):10.1111/nmo.13101. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13101. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 28485065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Focus on Enterochromaffin Cells among the Enteroendocrine Cells: Localization, Morphology, and Role.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 29;23(7):3758. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073758. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rfx6 promotes the differentiation of peptide-secreting enteroendocrine cells while repressing genetic programs controlling serotonin production.Mol Metab. 2019 Nov;29:24-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.08.007. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31668390 Free PMC article.
-
Stratification of enterochromaffin cells by single-cell expression analysis.Elife. 2025 Apr 4;12:RP90596. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90596. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40184163 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study in Vestibular Neuritis: Involvement of the Host Factor for HSV-1 Replication.Front Neurol. 2018 Jul 20;9:591. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00591. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30079052 Free PMC article.
-
The association between microbial community and ileal gene expression on intestinal wall thickness alterations in chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Apr;99(4):1847-1861. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.029. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32241465 Free PMC article.
-
ISX-9 manipulates endocrine progenitor fate revealing conserved intestinal lineages in mouse and human organoids.Mol Metab. 2020 Apr;34:157-173. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.01.012. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32180555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson K. R., Torres C. A., Solomon K., Becker T. C., Newgard C. B., Wright C. V., Hagman J. and Sussel L. (2009). Cooperative transcriptional regulation of the essential pancreatic islet gene NeuroD1 (beta2) by Nkx2.2 and neurogenin 3. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 31236-31248. 10.1074/jbc.M109.048694 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artis D., Wang M. L., Keilbaugh S. A., He W., Brenes M., Swain G. P., Knight P. A., Donaldson D. D., Lazar M. A., Miller H. R. P. et al. (2004). RELMbeta/FIZZ2 is a goblet cell-specific immune-effector molecule in the gastrointestinal tract. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 13596-13600. 10.1073/pnas.0404034101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

