Effect of salt intake on beat-to-beat blood pressure nonlinear dynamics and entropy in salt-sensitive versus salt-protected rats
- PMID: 27288061
- PMCID: PMC4908498
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12823
Effect of salt intake on beat-to-beat blood pressure nonlinear dynamics and entropy in salt-sensitive versus salt-protected rats
Abstract
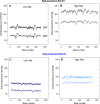
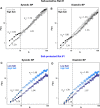
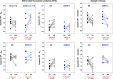
Blood pressure exhibits substantial short- and long-term variability (BPV). We assessed the hypothesis that the complexity of beat-to-beat BPV will be differentially altered in salt-sensitive hypertensive Dahl rats (SS) versus rats protected from salt-induced hypertension (SSBN13) maintained on high-salt versus low-salt diet. Beat-to-beat systolic and diastolic BP series from nine SS and six SSBN13 rats (http://www.physionet.org) were analyzed following 9 weeks on low salt and repeated after 2 weeks on high salt. BP complexity was quantified by detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA), short- and long-range scaling exponents (αS and αL), sample entropy (SampEn), and traditional standard deviation (SD) and coefficient of variation (CV(%)). Mean systolic and diastolic BP increased on high-salt diet (P < 0.01) particularly for SS rats. SD and CV(%) were similar across groups irrespective of diet. Salt-sensitive and -protected rats exhibited similar complexity indices on low-salt diet. On high salt, (1) SS rats showed increased scaling exponents or smoother, systolic (P = 0.007 [αL]) and diastolic (P = 0.008 [αL]) BP series; (2) salt-protected rats showed lower SampEn (less complex) systolic and diastolic BP (P = 0.046); and (3) compared to protected SSBN13 rats, SS showed higher αL for systolic (P = 0.01) and diastolic (P = 0.005) BP Hypertensive SS rats are more susceptible to high salt with a greater rise in mean BP and reduced complexity. Comparable mean pressures in sensitive and protective rats when on low-salt diet coupled with similar BPV dynamics suggest a protective role of low-salt intake in hypertensive rats. This effect likely reflects better coupling of biologic oscillators.
Keywords: Beat‐to‐beat variability; complexity; detrended fluctuation analysis.
© 2016 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of High Dietary Sodium Consumption on Blood Pressure Variability in Healthy, Young Adults.Am J Hypertens. 2020 Apr 29;33(5):422-429. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa014. Am J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32006422 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adenosine Receptors Influence Hypertension in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats: Dependence on Receptor Subtype, Salt Diet, and Sex.Hypertension. 2018 Aug;72(2):511-521. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10765. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Hypertension. 2018. PMID: 29941515 Free PMC article.
-
Is renal ß-adrenergic-WNK4-NCC pathway important in salt hypertension of Dahl rats?Physiol Res. 2019 Dec 30;68(6):873-882. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934334. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Physiol Res. 2019. PMID: 31647304
-
Cooperation of augmented calcium sensitization and increased calcium entry contributes to high blood pressure in salt-sensitive Dahl rats.Hypertens Res. 2021 Sep;44(9):1067-1078. doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00659-5. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Hypertens Res. 2021. PMID: 33875859
-
A Meta-Analysis of Effect of Dietary Salt Restriction on Blood Pressure in Chinese Adults.Glob Heart. 2015 Dec;10(4):291-299.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.gheart.2014.10.009. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Glob Heart. 2015. PMID: 26014655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Capacity of Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Variability for Cardioautonomic and Vascular Dysfunction in Early Metabolic Challenge.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 24;13:902582. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.902582. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35814210 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide map of proximity linkage to renin proximal promoter in rat.Physiol Genomics. 2018 May 1;50(5):323-331. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00132.2017. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29521603 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal study on the effect of surgical weight loss on beat-to-beat blood pressure variability in patients undergoing bariatric surgery: a study protocol.BMJ Open. 2021 Oct 19;11(10):e050957. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050957. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34667007 Free PMC article.
-
Amplitude- and Fluctuation-Based Dispersion Entropy.Entropy (Basel). 2018 Mar 20;20(3):210. doi: 10.3390/e20030210. Entropy (Basel). 2018. PMID: 33265301 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on the Autonomic Nervous System and Cardiovascular System in Rats in a Sex-Specific Manner.Pediatr Rep. 2024 Apr 9;16(2):278-287. doi: 10.3390/pediatric16020024. Pediatr Rep. 2024. PMID: 38651463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cerutti, S. , Corino V. D., Mainardi L., Lombardi F., Aktaruzzaman M., and Sassi R.. 2014. Non‐linear regularity of arterial blood pressure variability in patient with atrial fibrillation in tilt‐test procedure. Europace 16:iv141–iv147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

