Neuroimaging cognitive reappraisal in clinical populations to define neural targets for enhancing emotion regulation. A systematic review
- PMID: 27288319
- PMCID: PMC5145785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.06.009
Neuroimaging cognitive reappraisal in clinical populations to define neural targets for enhancing emotion regulation. A systematic review
Abstract
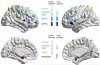
Reduced capacity to cognitively regulate emotional responses is a common impairment across major neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain systems supporting one such strategy, cognitive reappraisal of emotion, have been investigated extensively in the healthy population, a research focus that has led to influential meta-analyses and literature reviews. However, the emerging literature on neural substrates underlying cognitive reappraisal in clinical populations is yet to be systematically reviewed. Therefore, the goal of the current review was to summarize the literature on cognitive reappraisal and highlight common and distinct neural correlates of impaired emotion regulation in clinical populations. We performed a two-stage systematic literature search, selecting 32 studies on cognitive reappraisal in individuals with mood disorders (n=12), anxiety disorders (n=14), addiction (n=2), schizophrenia (n=2), and personality disorders (n=5). Comparing findings across these disorders allowed us to determine underlying mechanisms that were either disorder-specific or common across disorders. Results showed that across clinical populations, individuals consistently demonstrated reduced recruitment of the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC) and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) during downregulation of negative emotion, indicating that there may be a core deficit in selection, manipulation and inhibition during reappraisal. Further, in individuals with mood disorders, amygdala responses were enhanced during downregulation of emotion, suggesting hyperactive bottom-up responses or reduced modulatory capacity. In individuals with anxiety disorders, however, emotion regulation revealed reduced activity in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and inferior/superior parietal cortex, possibly indicating a deficit in allocation of attention. The reviewed studies thus provide evidence for both disorder-specific and common deficits across clinical populations. These findings highlight the role of distinct neural substrates as targets for developing/assessing novel therapeutic approaches that are geared towards cognitive regulation of emotion, as well as the importance of transdiagnostic research to identify both disorder specific and core mechanisms.
Keywords: Anxiety disorder; Depression; EEG; Emotion regulation; RDoC; fMRI.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Albein-Urios N, Verdejo-Román J, Asensio S, Soriano-Mas C, Martínez-González JM, Verdejo-García A. Re-appraisal of negative emotions in cocaine dependence: Dysfunctional corticolimbic activation and connectivity. Addiction Biology. 2014;19:415–426. doi:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00497.x. - PubMed
-
- Beauregard M, Paquette V, Lévesque J. Dysfunction in the neural circuitry of emotional self-regulation in major depressive disorder. Neuroreport. 2006;17(8):843–846. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000220132.32091.9f. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Rush AJ, Shaw BF, Emery G. Cognitive Therapy of Depression. The Guilford Press; New York: 1979.
-
- Blair KS, Geraci M, Smith BW, Hollon N, DeVido J, Otero M, Pine DS. Reduced dorsal anterior cingulate cortical activity during emotional regulation and top-down attentional control in generalized social phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, and comorbid generalized social phobia/generalized anxiety disorder. Biological Psychiatry. 2012;72(6):476–82. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.04.013. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

