Expression of TRPC6 and BDNF in Cortical Lesions From Patients With Focal Cortical Dysplasia
- PMID: 27288906
- PMCID: PMC4940447
- DOI: 10.1093/jnen/nlw044
Expression of TRPC6 and BDNF in Cortical Lesions From Patients With Focal Cortical Dysplasia
Abstract
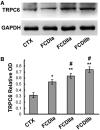
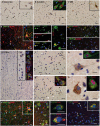
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) likely results from abnormal migration of neural progenitor cells originating from the subventricular zone. To elucidate the roles in molecules that are involved in neural migration pathway abnormalities in FCDs, we investigated the expression patterns of transient receptor potential canonical channel 6 (TRPC6) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in cortical lesions from FCD patients and in samples of normal control cortex. TRPC6 and BDNF mRNA and protein levels were increased in FCD lesions. By immunohistochemistry, they were strongly expressed in microcolumns, heterotopic neurons, dysmorphic neurons, and balloon cells (BCs). Colocalization assays revealed that most of the misshapen TRPC6-positive or heterotopic cells had a neuronal lineage with the exception of TRPC6-positive FCDiib patient BCs, which had both neuronal and glial features. Most TRPC6-positive cells were glutamatergic neurons. There was also greater expression of calmodulin-dependent kinase IV (CaMKIV), the downstream factor of TRPC6, in FCD lesions, suggesting that TRPC6 expression promoted dendritic growth and the development of dendritic spines and excitatory synapses via the CaMKIV-CREB pathway in FCD. Thus, overexpression of BDNF and TRPC6 and activation of the TRPC6 signal transduction pathway in cortical lesions of FCD patients may contribute to FC pathogenesis and epileptogenesis.
Keywords: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Epilepsy; Focal cortical dysplasia; Malformations of cortical development; Transient receptor potential canonical channel 6.
© 2016 American Association of Neuropathologists, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression of pannexin 1 and 2 in cortical lesions from intractable epilepsy patients with focal cortical dysplasia.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):6883-6895. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14317. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036289 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Patterns of TRPC1 in Cortical Lesions from Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Oct;57(2):265-72. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0615-5. Epub 2015 Aug 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26280213
-
Increased expression of fibroblast growth factor 13 in cortical lesions of the focal cortical dysplasia.Brain Res Bull. 2021 Mar;168:36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.11.023. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Brain Res Bull. 2021. PMID: 33285262
-
Focal Cortical Dysplasias: clinical implication of neuropathological classification systems.Acta Neuropathol. 2010 Sep;120(3):359-67. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0714-x. Epub 2010 Jul 4. Acta Neuropathol. 2010. PMID: 20607544 Review.
-
Focal cortical dysplasia: Molecular disturbances and clinicopathological classification (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2016 Nov;38(5):1327-1337. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2760. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 28025990 Review.
Cited by
-
Relevance of Abnormal KCNN1 Expression and Osmotic Hypersensitivity in Ewing Sarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 1;14(19):4819. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194819. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230742 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin Cannot Reduce Seizure Susceptibility in Infantile Rats with Malformations of Cortical Development Lacking mTORC1 Activation.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Dec;59(12):7439-7449. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03033-9. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36194361
-
The Role of TRPC6 in the Neuroprotection of Calycosin Against Cerebral Ischemic Injury.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 8;7(1):3039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03404-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28596571 Free PMC article.
-
Balloon cells in malformations of cortical development: friends or foes?Acta Epileptol. 2024 Jun 14;6(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s42494-024-00164-5. Acta Epileptol. 2024. PMID: 40217486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Estrogen Through BDNF-Transient Receptor Potential Channels 6 Signaling Pathway in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Perimenopausal Depression.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 8;14:869274. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.869274. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35875795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmini A, Holthausen H. Focal malformations of cortical development: A most relevant etiology of epilepsy in children. Handb Clin Neurol 2013;111:549–65 - PubMed
-
- Schwartzkroin PA, Walsh CA. Cortical malformations and epilepsy. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2000;6:268–80 - PubMed
-
- Mischel PS, Nguyen LP, Vinters HV. Cerebral cortical dysplasia associated with pediatric epilepsy. Review of neuropathologic features and proposal for a grading system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1995;54:137–53 - PubMed
-
- Crino PB, Eberwine J. Cellular and molecular basis of cerebral dysgenesis. J Neurosci Res 1997;50:907–16 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

