Fragment-Based Identification of Influenza Endonuclease Inhibitors
- PMID: 27291165
- PMCID: PMC4948595
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00628
Fragment-Based Identification of Influenza Endonuclease Inhibitors
Erratum in
-
Correction to Fragment-Based Identification of Influenza Endonuclease Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2017 Dec 14;60(23):9912. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01683. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29195040 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
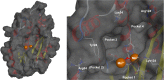
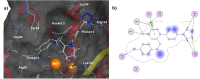
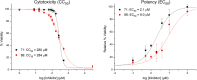
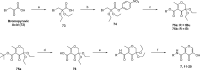
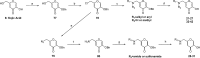
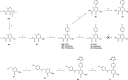
The influenza virus is responsible for millions of cases of severe illness annually. Yearly variance in the effectiveness of vaccination, coupled with emerging drug resistance, necessitates the development of new drugs to treat influenza infections. One attractive target is the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase PA subunit. Herein we report the development of inhibitors of influenza PA endonuclease derived from lead compounds identified from a metal-binding pharmacophore (MBP) library screen. Pyromeconic acid and derivatives thereof were found to be potent inhibitors of endonuclease. Guided by modeling and previously reported structural data, several sublibraries of molecules were elaborated from the MBP hits. Structure-activity relationships were established, and more potent molecules were designed and synthesized using fragment growth and fragment merging strategies. This approach ultimately resulted in the development of a lead compound with an IC50 value of 14 nM, which displayed an EC50 value of 2.1 μM against H1N1 influenza virus in MDCK cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

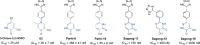


References
-
- Adjusted vaccine effectiveness estimates for influenza seasons from 2005 to 2015. http://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/vaccination/effectiveness-studies.htm (accessed February 26, 2016).
-
- Monod A.; Swale C.; Tarus B.; Tissot A.; Delmas B.; Ruigrok R. W.; Crepin T.; Slama-Schwok A. Learning from structure-based drug design and new antivirals targeting the ribonucleoprotein complex for the treatment of influenza. Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 2015, 10 (4), 345–371. 10.1517/17460441.2015.1019859. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

