Septic arthritis due to tubercular and Aspergillus co-infection
- PMID: 27293296
- PMCID: PMC4885304
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5413.181783
Septic arthritis due to tubercular and Aspergillus co-infection
Abstract
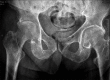
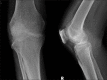
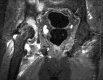
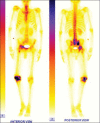
Aspergillus septic arthritis is a rare and serious medical and surgical problem. It occurs mainly in immunocompromised patients. Aspergillus fumigatus is the most common causative organism followed by Aspergillus flavus. The most common site affected is knee followed by shoulder, ankle, wrist, hip and sacroiliac joint. Debridement and voriconazole are primary treatment of articular aspergilosis. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reported cases of co-infection of tuberculosis (TB) and Aspergillus infecting joints. We report a case of co-infection of TB and A. flavus of hip and knee of a 60-year-old male, with type 2 diabetes mellitus. He was treated with debridement, intravenous voriconazole, and antitubercular drugs.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Aspergillus flavus; arthritis; aspergillus septic arthritis; fungi; infections; joint tuberculosis; septic; tuberculosis; voriconazole.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Golmia R, Bello I, Marra A, Hamerschlak N, Osawa A, Scheinberg M. Aspergillus fumigatus joint infection: A review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011;40:580–4. - PubMed
-
- Dal T, Tekin A, Deveci Ö, Bulut M, Fırat U, Mete M. Septic arthritis caused by Aspergillus fumigatus in an immunosuppressive patient: A case report and review of the literature. J Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2012;2:29–32.
-
- Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, et al. Treatment of aspergillosis: Clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:327–60. - PubMed
-
- Kaya A, Topu Z, Fitoz S, Numanoglu N. Pulmonary tuberculosis with multifocal skeletal involvement. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2004;61:133–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
