Shikonin Attenuates Concanavalin A-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibition of the JNK Pathway
- PMID: 27293314
- PMCID: PMC4884842
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2748367
Shikonin Attenuates Concanavalin A-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibition of the JNK Pathway
Abstract
Objective: Shikonin possesses anti-inflammatory effects. However, its function in concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury remains uncertain. The aim of the present study was to investigate the functions of shikonin and its mechanism of protection on ConA-induced acute liver injury.
Materials and methods: Balb/C mice were exposed to ConA (20 mg/kg) via tail vein injection to establish acute liver injury; shikonin (7.5 mg/kg and 12.5 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally administered 2 h before the ConA injection. The serum liver enzyme levels and the inflammatory cytokine levels were determined at 3, 6, and 24 h after ConA injection.
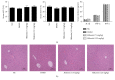
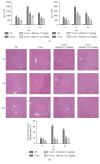
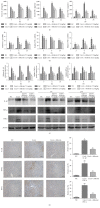
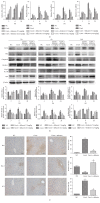
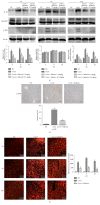
Results: After the injection of ConA, inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were significantly increased. Shikonin significantly ameliorated liver injury and histopathological changes and suppressed the release of inflammatory cytokines. The expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax were markedly affected by shikonin pretreatment. LC3, Beclin-1, and p-JNK expression levels were decreased in the shikonin-pretreated groups compared with the ConA-treated groups. Shikonin attenuated ConA-induced liver injury by reducing apoptosis and autophagy through the inhibition of the JNK pathway.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that shikonin pretreatment attenuates ConA-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy through the suppression of the JNK pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
15d-PGJ2 alleviates ConA-induced acute liver injury in mice by up-regulating HO-1 and reducing hepatic cell autophagy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 May;80:183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27133055
-
Protective effects of necrostatin-1 against concanavalin A-induced acute hepatic injury in mice.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:706156. doi: 10.1155/2013/706156. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 24198446 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108704. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108704. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30818140
-
Salvianolic acid A preconditioning confers protection against concanavalin A-induced liver injury through SIRT1-mediated repression of p66shc in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 15;273(1):68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23993977
-
The Protective Effects of Levo-Tetrahydropalmatine on ConA-Induced Liver Injury Are via TRAF6/JNK Signaling.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 4;2018:4032484. doi: 10.1155/2018/4032484. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30622431 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Salvianolic acid B protects against acute and chronic liver injury by inhibiting Smad2C/L phosphorylation.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Apr;21(4):341. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9772. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33732314 Free PMC article.
-
In silico Identification and Mechanism Exploration of Hepatotoxic Ingredients in Traditional Chinese Medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 3;10:458. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00458. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31130860 Free PMC article.
-
The liver protection of propylene glycol alginate sodium sulfate preconditioning against ischemia reperfusion injury: focusing MAPK pathway activity.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 9;7(1):15175. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15521-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29123239 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of natural compounds in anti-liver fibrosis by affecting autophagy of hepatic stellate cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Feb;48(2):1915-1924. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06171-w. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33609264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
L-Theanine Mitigates Acute Alcoholic Intestinal Injury by Activating the HIF-1 Signaling Pathway to Regulate the TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α Axis in Mice.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 18;17(4):720. doi: 10.3390/nu17040720. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40005048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaneko Y., Harada M., Kawano T., et al. Augmentation of Vα14 NKT cell-mediated cytotoxicity by interleukin 4 in an autocrine mechanism resulting in the development of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2000;191(1):105–114. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.1.105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

