Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus: clinical characteristics and prognostic evaluation of 49 cases with surgical resection
- PMID: 27293844
- PMCID: PMC4886019
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2016.04.21
Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus: clinical characteristics and prognostic evaluation of 49 cases with surgical resection
Abstract
Background: The clinicopathological features and optimum treatment of esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC) are hardly known due to its rarity. Therefore, we conducted a retrospective study to analyze the clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with surgically resected esophageal NEC.
Methods: We collected clinicopathological data on consecutive limited disease stage esophageal NEC patients who underwent esophagectomy with regional lymphadenectomy in West China Hospital from January 2007 to December 2013.
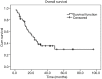
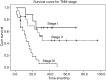
Results: A total of forty-nine patients were analyzed retrospectively. The mean age of the patients was 58.4±8.2 years with male predominance. Fifty-five percent of the esophageal NEC were located in the middle thoracic esophagus. Histologically, 28 (57.1%) patients were found to be small cell NECs. Fifty-one percent of the patients were found to have lymph node metastasis. According to the 2009 American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, 9 patients were at stage I, 21 patients stage II, and 19 patients stage III. Twenty-six patients (53.1%) received adjuvant therapy. After a median follow-up of 44.8 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 35.2-50.4 months], the median survival time of the patients was 22.4 months (95% CI, 14.0-30.8 months). The 1-year and 3-year survival rates for the whole cohort patients were 74.9% and 35.3%, respectively. In univariate analysis, TNM staging, lymph node metastasis and adjutant therapy significantly influenced survival time. In multivariate analysis, TNM staging was the only independent prognostic factor.
Conclusions: Esophageal NEC has a poor prognosis. The 2009 AJCC TNM staging system for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma may also fit for esophageal NEC. Surgery combined with adjuvant therapy may be a good option for treating limited disease stage esophageal NEC. Further prospective studies defining the optimum therapeutic regimen for esophageal NEC are needed.
Keywords: Neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC); esophagus; prognosis; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Is There a Role for Surgery in Treating Localized Esophageal Neuroendocrine Tumor?Ann Surg Oncol. 2020 Mar;27(3):960-961. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-08118-9. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31828688 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
[Prognostic analysis of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;36(8):612-6. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25430029 Chinese.
-
The Role of Surgery in Treating Resectable Limited Disease of Esophageal Neuroendocrine Carcinoma.World J Surg. 2018 Aug;42(8):2428-2436. doi: 10.1007/s00268-018-4475-3. World J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29340724
-
Evaluation of the 7th edition of the TNM classification in patients with resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 28;20(48):18397-403. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18397. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25561808 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Gall Bladder: A Series of 19 Cases with Review of Literature.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2015 Dec;46(4):356-64. doi: 10.1007/s12029-015-9745-9. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26208508 Review.
-
Systematic review of case reports of Japanese esophageal neuroendocrine cell carcinoma in the Japanese literature.Int Cancer Conf J. 2019 Feb 18;8(2):47-57. doi: 10.1007/s13691-019-00359-5. eCollection 2019 Apr. Int Cancer Conf J. 2019. PMID: 31149547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology, prognostic factors, and survival analysis in small cell esophageal carcinoma: A population-based study with external validation.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Apr 3;25(5):1009-1022. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.11090. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39226115 Free PMC article.
-
Validation and proposed modification of the 8th edition American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for patients with esophageal neuroendocrine neoplasms: Evaluation of a revised lymph node classification.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jun;19(6):4122-4132. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11480. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32382351 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors and Predictive Score Model for Early Recurrence After Curative Surgery in Patients With Poorly Differentiated Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms.Front Surg. 2021 Sep 16;8:703138. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.703138. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34604293 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Treatment With Nivolumab Contributes to Long-Term Survival in a Case of Unresectable Esophagogastric Junction Neuroendocrine Carcinoma.Cureus. 2024 Aug 1;16(8):e65981. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65981. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39221328 Free PMC article.
-
The clinicopathologic features and prognosis of esophageal neuroendocrine carcinomas: a single-center study of 53 resection cases.BMC Cancer. 2019 Dec 18;19(1):1234. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6420-8. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31852479 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources