Therapeutic evaluation of monoclonal antibody-maytansinoid conjugate as a model of RON-targeted drug delivery for pancreatic cancer treatment
- PMID: 27293990
- PMCID: PMC4889711
Therapeutic evaluation of monoclonal antibody-maytansinoid conjugate as a model of RON-targeted drug delivery for pancreatic cancer treatment
Abstract
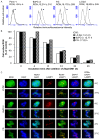
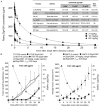
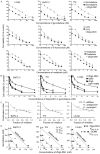
Aberrant expression of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase, a member of the MET proto-oncogene family, contributes significantly to pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis and chemoresistance. Here we validate RON as a target for pancreatic cancer therapy using a novel anti-RON antibody Zt/g4-drug maytansinoid conjugates (Zt/g4-DM1) as a model for RON-targeted drug delivery to kill pancreatic cancer cells. In pancreatic cancer cell lines overexpressing RON, Zt/g4-DM1 rapidly induced receptor endocytosis, arrested cell cycle at G2/M phase, reduced cell viability, and subsequently caused massive cell death. These in vitro observations help to establish a correlation between the number of the cell surface RON receptors and the efficacy of Zt/g4-DM1 in reduction of cell viability. In mice, Zt/g4-DM1 pharmacokinetics in the linear dose range fitted into a two-compartment model with clearance in 0.21 ml/day/kg and terminal half-life at 6.05 days. These results helped to confirm a concentration-activity relationship for the BxPC-3 and other pancreatic cancer cell xenograft model with a tumoristatic dose at 3.02 mg/kg. Zt/g4-DM1 was effective in vivo against various xenograft PDAC growth but efficacy varied with individual cell lines. Combination of Zt/g4-DM1 with gemcitabine had a complete inhibition of xenograft pancreatic cancer growth. We conclude from these studies that increased RON expression in pancreatic cancer cells is a suitable targeting moiety for anti-RON ADC-directed drug delivery and anticancer therapy. Zt/g4-DM1 is highly effective alone or in combination with chemotherapeutics in inhibition of pancreatic cancer xenograft growth in preclinical models. These findings justify the use of humanized Zt/g4-DM1 for targeted pancreatic cancer therapy in the future.
Keywords: Receptor tyrosine kinase; antibody-drug conjugate; combination therapy; pancreatic cancer; pharmacokinetics; therapeutic efficacy; xenograft tumor model.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MET and RON receptor tyrosine kinases in colorectal adenocarcinoma: molecular features as drug targets and antibody-drug conjugates for therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 22;39(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01711-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32962738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological evaluation of antibody-maytansinoid conjugates as a strategy of RON targeted drug delivery for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Apr 22;35:70. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0347-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27102688 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of anti-RON antibody Zt/g4-drug maytansinoid conjugation (Anti-RON ADC) as a novel therapeutics for targeted colorectal cancer therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 1;20(23):6045-58. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0898. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25294907
-
Preclinical Efficacy of Anti-RON Antibody-Drug Conjugate Zt/g4-MMAE for Targeted Therapy of Pancreatic Cancer Overexpressing RON Receptor Tyrosine Kinase.Mol Pharm. 2018 Aug 6;15(8):3260-3271. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00298. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29944378
-
Potential therapeutics specific to c-MET/RON receptor tyrosine kinases for molecular targeting in cancer therapy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Sep;31(9):1181-8. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.106. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20694025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Humanized dual-targeting antibody-drug conjugates specific to MET and RON receptors as a pharmaceutical strategy for the treatment of cancers exhibiting phenotypic heterogeneity.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May;46(5):1375-1389. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01458-7. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39837982 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant RON and MET Co-overexpression as Novel Prognostic Biomarkers of Shortened Patient Survival and Therapeutic Targets of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Pancreatic Cancer.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 5;9:1377. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01377. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31867280 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-Drug Conjugates of Active Metabolites of Nucleoside Analogs and Cytotoxic Agents Inhibit Pancreatic Tumor Cell Growth.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Mar 17;6:80-88. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 28325302 Free PMC article.
-
MET and RON receptor tyrosine kinases in colorectal adenocarcinoma: molecular features as drug targets and antibody-drug conjugates for therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 22;39(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01711-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32962738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of a novel humanized antibody-drug conjugate recognizing plexin-semaphorin-integrin domain in the RON receptor for targeted cancer therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Sep 13;7(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0732-8. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31519211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1039–1049. - PubMed
-
- Vaccaro V, Gelibter A, Bria E, Iapicca P, Cappello P, Di Modugno F, Pino MS, Nuzzo C, Cognetti F, Novelli F, Nistico P, Milella M. Molecular and genetic bases of pancreatic cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 2012;13:731–743. - PubMed
-
- Bardeesy N, DePinho RA. Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:897–909. - PubMed
-
- Jamieson NB, Carter CR, McKay CJ, Oien KA. Tissue biomarkers for prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:3316–3331. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
