Improvement of gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells by RUNX2 depletion-mediated augmentation of TAp73-dependent cell death
- PMID: 27294865
- PMCID: PMC4945741
- DOI: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.40
Improvement of gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells by RUNX2 depletion-mediated augmentation of TAp73-dependent cell death
Abstract
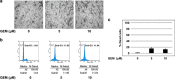
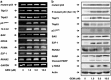
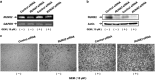
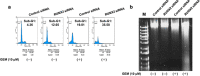
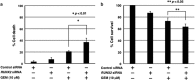
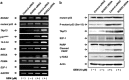
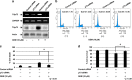
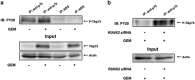
Pancreatic cancer exhibits the worst prognostic outcome among human cancers. Recently, we have described that depletion of RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine (GEM) sensitivity of p53-deficient pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells through the activation of TAp63-mediated cell death pathway. These findings raised a question whether RUNX2 silencing could also improve GEM efficacy on pancreatic cancer cells bearing p53 mutation. In the present study, we have extended our study to p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells. Based on our current results, MiaPaCa-2 cells were much more resistant to GEM as compared with p53-proficient pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells, and there existed a clear inverse relationship between the expression levels of TAp73 and RUNX2 in response to GEM. Forced expression of TAp73α in MiaPaCa-2 cells significantly promoted cell cycle arrest and/or cell death, indicating that a large amount of TAp73 might induce cell death even in the presence of mutant p53. Consistent with this notion, overexpression of TAp73α stimulated luciferase activity driven by p53/TAp73-target gene promoters in MiaPaCa-2 cells. Similar to AsPC-1 cells, small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of RUNX2 remarkably enhanced GEM sensitivity of MiPaCa-2 cells. Under our experimental conditions, TAp73 further accumulated in RUNX2-depleted MiaPaCa-2 cells exposed to GEM relative to GEM-treated non-silencing control cells. As expected, silencing of p73 reduced GEM sensitivity of MiPaCa-2 cells. Moreover, GEM-mediated Tyr phosphorylation level of TAp73 was much more elevated in RUNX2-depleted MiaPaCa-2 cells. Collectively, our present findings strongly suggest that knockdown of RUNX2 contributes to a prominent enhancement of GEM sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer cells through the activation of TAp73-mediated cell death pathway, and also provides a promising strategy for the treatment of patients with pancreatic cancer bearing p53 mutation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4217-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29558908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depletion of pro-oncogenic RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine (GEM) sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer Panc-1 cells through the induction of pro-apoptotic TAp63.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):71937-71950. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12433. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713122 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-deficient human pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells through the stimulation of TAp63-mediated cell death.Cell Death Discov. 2015 Aug 10;1:15010. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.10. eCollection 2015. Cell Death Discov. 2015. PMID: 27551445 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) enhances SAHA sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer cells through the regulation of mutant p53 and TAp63.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 3;12(7):e0179884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179884. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28671946 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Role of p53 and TAp73 in Neuroblastoma: From Pathogenesis to Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;14(24):6212. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246212. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The COL11A1/Akt/CREB signaling axis enables mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic evasion to promote chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells through modulating BAX/BCL-2 function.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(5):1406-1420. doi: 10.7150/jca.47032. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33531986 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4217-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29558908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX2 Reverses p53-Induced Chemotherapy Resistance in Gastric Cancer.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023 Mar 27;16:253-261. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S394393. eCollection 2023. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37009416 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Evaluation of an Opioid Growth Factor Bioconjugate Targeting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 16;16(2):283. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020283. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399336 Free PMC article.
-
A ferrocene-containing nucleoside analogue targets DNA replication in pancreatic cancer cells.Metallomics. 2022 Jul 25;14(7):mfac041. doi: 10.1093/mtomcs/mfac041. Metallomics. 2022. PMID: 35689667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2011; 74: 2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Oettle H, Neuhaus P, Hochhaus A, Hartmann JT, Gellert K, Ridwelski K et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and long-term outcomes among patients with resected PDAC: The conko-001 randomized trial. JAMA 2013; 310: 1473–1481. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

