Anti-Human Endoglin (hCD105) Immunotoxin-Containing Recombinant Single Chain Ribosome-Inactivating Protein Musarmin 1
- PMID: 27294959
- PMCID: PMC4926150
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8060184
Anti-Human Endoglin (hCD105) Immunotoxin-Containing Recombinant Single Chain Ribosome-Inactivating Protein Musarmin 1
Abstract
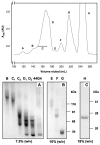
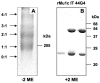
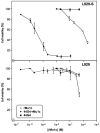
Endoglin (CD105) is an accessory component of the TGF-β receptor complex, which is expressed in a number of tissues and over-expressed in the endothelial cells of tumor neovasculature. Targeting endoglin with immunotoxins containing type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins has proved an effective tool to reduce blood supply to B16 mice tumor xenografts. We prepared anti-endoglin immunotoxin (IT)-containing recombinant musarmin 1 (single chain ribosome-inactivating proteins) linked to the mouse anti-human CD105 44G4 mouse monoclonal antibody via N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio) propionate (SPDP). The immunotoxin specifically killed L929 fibroblast mouse cells transfected with the short form of human endoglin with IC50 values in the range of 5 × 10(-10) to 10(-9) M.
Keywords: 44G4; CD105; anti-endoglin monoclonal antibody; anti-tumor therapy; cancer therapy; endoglin; recombinant musarmin.
Figures

References
-
- Weidle U.H., Tiefenthaler G., Schiller C., Weiss E.H., Georges G., Brinkmann U. Prospects of bacterial and plant protein-based immunotoxins for treatment of cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2014;11:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Gilabert-Oriol R., Weng A., Mallinckrodt B., Melzig M.F., Fuchs H., Thakur M. Immunotoxins constructed with ribosome-inactivating proteins and their enhancers: A lethal cocktail with tumor specific efficacy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014;20:6584–6643. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140826153913. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

