Unconventional secretion of misfolded proteins promotes adaptation to proteasome dysfunction in mammalian cells
- PMID: 27295555
- PMCID: PMC10701763
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3372
Unconventional secretion of misfolded proteins promotes adaptation to proteasome dysfunction in mammalian cells
Abstract
To safeguard proteomic integrity, cells rely on the proteasome to degrade aberrant polypeptides, but it is unclear how cells remove defective proteins that have escaped degradation owing to proteasome insufficiency or dysfunction. Here we report a pathway termed misfolding-associated protein secretion, which uses the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated deubiquitylase USP19 to preferentially export aberrant cytosolic proteins. Intriguingly, the catalytic domain of USP19 possesses an unprecedented chaperone activity, allowing recruitment of misfolded proteins to the ER surface for deubiquitylation. Deubiquitylated cargos are encapsulated into ER-associated late endosomes and secreted to the cell exterior. USP19-deficient cells cannot efficiently secrete unwanted proteins, and grow more slowly than wild-type cells following exposure to a proteasome inhibitor. Together, our findings delineate a protein quality control (PQC) pathway that, unlike degradation-based PQC mechanisms, promotes protein homeostasis by exporting misfolded proteins through an unconventional protein secretion process.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

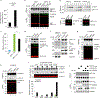
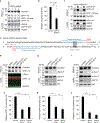

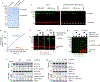
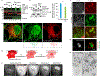
References
-
- Wolff S, Weissman JS & Dillin A. Differential scales of protein quality control. Cell 157, 52–64 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Bukau B, Weissman J. & Horwich A. Molecular chaperones and protein quality control. Cell 125, 443–451 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Buchberger A, Bukau B. & Sommer T. Protein quality control in the cytosol and the endoplasmic reticulum: brothers in arms. Mol. Cell 40, 238–252 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

