Transmembrane semaphorins: Multimodal signaling cues in development and cancer
- PMID: 27295627
- PMCID: PMC5160034
- DOI: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1197479
Transmembrane semaphorins: Multimodal signaling cues in development and cancer
Abstract
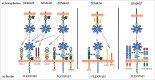
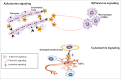
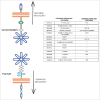
Semaphorins constitute a large family of membrane-bound and secreted proteins that provide guidance cues for axon pathfinding and cell migration. Although initially discovered as repelling cues for axons in nervous system, they have been found to regulate cell adhesion and motility, angiogenesis, immune function and tumor progression. Notably, semaphorins are bifunctional cues and for instance can mediate both repulsive and attractive functions in different contexts. While many studies focused so far on the function of secreted family members, class 1 semaphorins in invertebrates and class 4, 5 and 6 in vertebrate species comprise around 14 transmembrane semaphorin molecules with emerging functional relevance. These can signal in juxtacrine, paracrine and autocrine fashion, hence mediating long and short range repulsive and attractive guidance cues which have a profound impact on cellular morphology and functions. Importantly, transmembrane semaphorins are capable of bidirectional signaling, acting both in "forward" mode via plexins (sometimes in association with receptor tyrosine kinases), and in "reverse" manner through their cytoplasmic domains. In this review, we will survey known molecular mechanisms underlying the functions of transmembrane semaphorins in development and cancer.
Keywords: cancer; development; plexins; semaphorins; signaling mechanisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transmembrane semaphorins, forward and reverse signaling: have a look both ways.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(8):1609-22. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2137-x. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26794845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin signals on the road to cancer invasion and metastasis.Cell Adh Migr. 2007 Apr-Jun;1(2):62-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.1.2.4570. Epub 2007 Apr 13. Cell Adh Migr. 2007. PMID: 19329883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Class-3 Semaphorins and Their Receptors: Potent Multifunctional Modulators of Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 28;20(3):556. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030556. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30696103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin regulation of cellular morphology.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:263-92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010605.093554. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17539753 Review.
-
Semaphorins and their Signaling Mechanisms.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1493:1-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6448-2_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27787839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaceted Functional Role of Semaphorins in Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 30;20(9):2144. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092144. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia and macrophages promote corralling, wound compaction and recovery after spinal cord injury via Plexin-B2.Nat Neurosci. 2020 Mar;23(3):337-350. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0597-7. Nat Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32112058 Free PMC article.
-
A reverse signaling pathway downstream of Sema4A controls cell migration via Scrib.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jan 2;216(1):199-215. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201602002. Epub 2016 Dec 22. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28007914 Free PMC article.
-
Current drug design to target the Semaphorin/Neuropilin/Plexin complexes.Cell Adh Migr. 2016 Nov;10(6):700-708. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1261785. Cell Adh Migr. 2016. PMID: 27906605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin signaling restricts neuronal regeneration in C. elegans.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 17;10:814160. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.814160. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36325362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tamagnone L, Artigiani S, Chen H, He Z, Ming GI, Song H, Chedotal A, Winberg ML, Goodman CS, Poo M, et al.. Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPI-anchored semaphorins in vertebrates. Cell 1999; 99:71-80; PMID:10520995; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80063-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai YT, Giger RJ, Ginty DD. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 1997; 90:753-62; PMID:9288754; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80535-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin AL, Ginty DD. Steering clear of semaphorins: neuropilins sound the retreat. Neuron 1997; 19:1159-62; PMID:9427240; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80408-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delgoffe GM, Woo SR, Turnis ME, Gravano DM, Guy C, Overacre AE, Bettini ML, Vogel P, Finkelstein D, Bonnevier J, et al.. Stability and function of regulatory T cells is maintained by a neuropilin-1-semaphorin-4a axis. Nature 2013; 501:252-6; PMID:23913274; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature12428 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tong Y, Hota PK, Penachioni JY, Hamaneh MB, Kim SJ, Alviani RS, Shen L, He H, Tempel W, Tamagnone L, et al.. Structure and function of the intracellular region of the Plexin-B1 transmembrane receptor. J Biol Chem 2009; 284:35962-72; PMID:19843518; http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.056275 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
