Diagnostic accuracy of resting left ventricular akinesia/hypokinesia in predicting abnormal coronary angiography
- PMID: 27295983
- PMCID: PMC4906607
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-016-0312-5
Diagnostic accuracy of resting left ventricular akinesia/hypokinesia in predicting abnormal coronary angiography
Abstract
Background: Although several reports demonstrate the efficacy of stress echocardiography in diagnosing coronary artery disease, comparable studies on the competence of the same imaging technique at rest are limited. This study aimed to evaluate whether ventricular akinesia/hypokinesia and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 55 % at rest are useful in predicting abnormal coronary angiography.
Methods: This study prospectively enrolled 100 diagnostic coronary catheterization candidates. Any routine echocardiography that the candidates had undergone before diagnostic coronary catheterization was reviewed. Patients were subclassified according to the presence and location of ventricular akinesia/hypokinesia, LVEF, and the results of diagnostic coronary catheterization. LVEF < 55 % was considered below the normal physiological limit. Abnormal coronary angiography was defined as narrowing of half or more of the caliber of at least one major coronary artery.
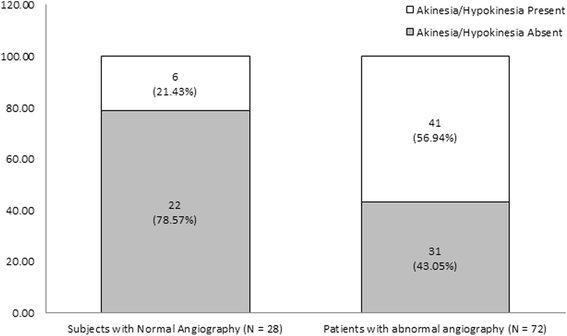
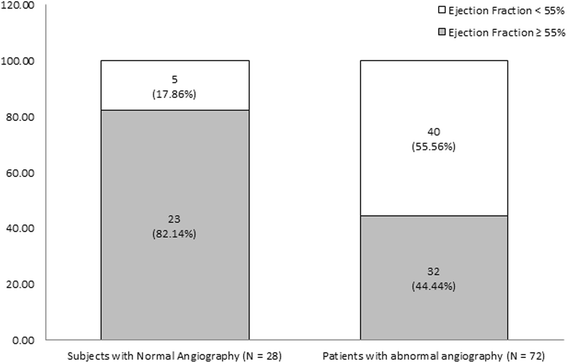
Results: Abnormal coronary angiography was significantly associated with akinesia/hypokinesia (OR = 4.85, P = 0.002) and LVEF < 55 % (OR = 5.75, P = 0.001). Screening of akinesia/hypokinesia and LVEF < 55 % as diagnostic tools for abnormal coronary angiography achieved comparable sensitivities (87.2 % vs. 88.9 %), specificities (41.5 vs. 41.8), and diagnostic accuracies (41.5 vs. 41.8). Left ventricular anterior wall akinesia/hypokinesia achieved a higher diagnostic odds ratio (9.7), sensitivity (95 %), and negative predictive value (96.4 %) compared with other types of akinesia/hypokinesia.
Conclusion: The overall diagnostic accuracy of akinesia/hypokinesia and LVEF < 55 % to predict abnormal coronary angiography was poor, probably owing to significant influences of macro- as well as micro-vascular ischemia on left ventricular function.
Keywords: Akinesia/hypokinesia; Coronary angiography; Coronary artery disease; Ejection fraction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extent and severity of coronary artery disease by coronary CT angiography is associated with elevated left ventricular diastolic pressures and worsening diastolic function.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2013 Sep-Oct;7(5):289-96.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Sep 26. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2013. PMID: 24268115
-
2-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography predicts severe coronary artery disease in women with normal left ventricular function: a case-control study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Aug 24;17(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0656-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 28836949 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of subclinical left and right ventricular dysfunctions measured by computed tomography angiography with the severity of coronary artery disease.Coron Artery Dis. 2011;22(6):380-7. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e328347506f. Coron Artery Dis. 2011. PMID: 21666441
-
Parametric Imaging for the Assessment of Cardiac Motion: A Review.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2018 Sep;9(3):377-393. doi: 10.1007/s13239-018-0362-1. Epub 2018 May 14. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2018. PMID: 29761408 Review.
-
Transthoracic echocardiographic imaging of coronary arteries: tips, traps, and pitfalls.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008 Feb 1;6:7. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-6-7. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008. PMID: 18241346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A simple prediction model to estimate obstructive coronary artery disease.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Jan 16;18(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0745-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29338684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demir H, Kahraman G, Isgoren S, Tan YZ, Kilic T, Berk F. Evaluation of post-stress left ventricular dysfunction and its relationship with perfusion abnormalities using gated SPECT in patients with cardiac syndrome X. Nucl Med Commun. 2008;29(3):208–14. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e3282f52c49. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical