Effects of 15 weeks of resistance exercise on pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in the vastus lateralis muscle of patients with fibromyalgia
- PMID: 27296860
- PMCID: PMC4906587
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1041-y
Effects of 15 weeks of resistance exercise on pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in the vastus lateralis muscle of patients with fibromyalgia
Abstract
Background: This study aimed at investigating the effect of a resistance exercise intervention on the interstitial muscle levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in fibromyalgia (FMS) and healthy controls (CON).
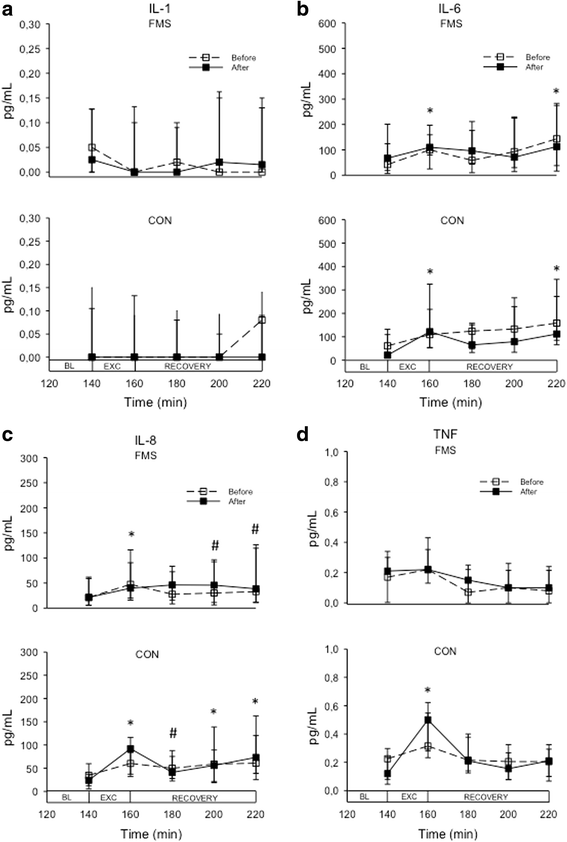
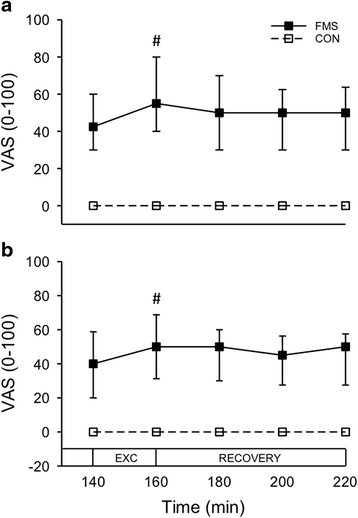
Methods: Twenty-four female patients with FMS (54 ± 8 years) and 27 female CON (54 ± 9 years) were subjected to intramuscular microdialysis of the most painful vastus lateralis muscle before and after 15 weeks of progressive resistance exercise twice per week. Baseline dialysates were sampled in the resting muscle 140 min after insertion of the microdialysis catheter. The participants then performed repetitive dynamic contractions (knee extension) for 20 min, followed by 60 min rest. Pain intensity was assessed with a 0-100 mm visual analogue scale (VAS), and fatigue was assessed with Borg's RPE throughout microdialysis. Dialysates were sampled every 20 min and analyzed with Luminex for interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha, IL-6, and IL-8.
Results: At both sessions and for both groups the dynamic contractions increased pain (P < 0.012) and fatigue (P < 0.001). The levels of TNF were lower in the FMS group than the CON group at both sessions (P < 0.05), but none of the other cytokines differed between the groups. IL-6 and IL-8 increased after the dynamic contractions in both groups (P < 0.010), while TNF increased only in CON (P < 0.05) and IL-1β did not change. Overall pain intensity was reduced after the 15 weeks of resistance exercise in FMS (P < 0.05), but there was no changes in fatigue or cytokine levels.
Conclusion: Progressive resistance exercise for 15 weeks did not affect the interstitial levels of IL-1β, TNF, IL-6, and IL-8 in the vastus lateralis muscle of FMS patients or CON.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01226784 , registered 21 October 2010.
Keywords: Cytokines; Dynamic contractions; Exercise; Fibromyalgia; Microdialysis; Quadriceps.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma Cytokine Levels in Fibromyalgia and Their Response to 15 Weeks of Progressive Resistance Exercise or Relaxation Therapy.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Apr 18;2018:3985154. doi: 10.1155/2018/3985154. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 29849487 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Levels of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Released in the Vastus Lateralis Muscle of Patients with Fibromyalgia and Healthy Controls during Contractions of the Quadriceps Muscle--A Microdialysis Study.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 1;10(12):e0143856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143856. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26624891 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance exercise improves muscle strength, health status and pain intensity in fibromyalgia--a randomized controlled trial.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jun 18;17(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0679-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26084281 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acute effects of physical exercises on the inflammatory markers of patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: A systematic review.J Neuroimmunol. 2018 Mar 15;316:40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 12. J Neuroimmunol. 2018. PMID: 29254627
-
The Impact of Acute and Chronic Exercise on Immunoglobulins and Cytokines in Elderly: Insights From a Critical Review of the Literature.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 14;12:631873. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.631873. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33936044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Electro-Muscle Stimulation Exercise Combined with Mat Pilates on Pain, Anxiety, and Strength in Sedentary Females with Fibromyalgia: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pers Med. 2024 Jun 28;14(7):697. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070697. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39063951 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of progressive intensity resistance training on the impact of fibromyalgia: protocol for a blinded randomized controlled trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Oct 14;24(1):816. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06952-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37838712 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Cytokine Levels in Fibromyalgia and Their Response to 15 Weeks of Progressive Resistance Exercise or Relaxation Therapy.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Apr 18;2018:3985154. doi: 10.1155/2018/3985154. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 29849487 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Elevated Perceived Exertion in People with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia: A Meta-analysis.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020 Dec;52(12):2615-2627. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002421. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020. PMID: 32555018 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids improve endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis: a study in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 May;188(2):208-218. doi: 10.1111/cei.12938. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28152574 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

