Lymphocyte-activation gene-3, an important immune checkpoint in cancer
- PMID: 27297395
- PMCID: PMC5021038
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12986
Lymphocyte-activation gene-3, an important immune checkpoint in cancer
Abstract
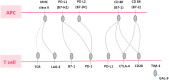
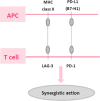
Immunotherapy has recently become widely used in lung cancer. Many oncologists are focused on cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and programmed cell death-1 (PD-1). Immunotherapy targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoints has shown promising efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but questions remain to be answered. Among them is whether the simultaneous inhibition of other checkpoints could improve outcomes. Lymphocyte-activation gene-3 (LAG-3) is another vital checkpoint that may have a synergistic interaction with PD-1/PD-L1. Here we review the LAG-3 function in cancer, clinical trials with agents targeting LAG-3 and the correlation of LAG-3 with other checkpoints.
Keywords: Cancer checkpoints; clinical trial; immunotherapy; lymphocyte-activation gene-3; soluble LAG-3.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Couzin‐Frankel J. Breakthrough of the year 2013. Cancer immunotherapy. Science 2013; 342: 1432–3. - PubMed
-
- Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7‐H1, a third member of the B7 family, co‐stimulates T‐cell proliferation and interleukin‐10 secretion. Nat Med 1999; 5: 1365–9. - PubMed
-
- Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR et al Tumor‐associated B7‐H1 promotes T‐cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med 2002; 8: 793–800. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R, Freeman GJ. The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 239–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials