Targeting RRM2 and Mutant BRAF Is a Novel Combinatorial Strategy for Melanoma
- PMID: 27297629
- PMCID: PMC5025362
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0099
Targeting RRM2 and Mutant BRAF Is a Novel Combinatorial Strategy for Melanoma
Abstract
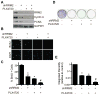
The majority of patients with melanoma harbor mutations in the BRAF oncogene, thus making it a clinically relevant target. However, response to mutant BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) is relatively short-lived with progression-free survival of only 6 to 7 months. Previously, we reported high expression of ribonucleotide reductase M2 (RRM2), which is rate-limiting for de novo dNTP synthesis, as a poor prognostic factor in patients with mutant BRAF melanoma. In this study, the notion that targeting de novo dNTP synthesis through knockdown of RRM2 could prolong the response of melanoma cells to BRAFi was investigated. Knockdown of RRM2 in combination with the mutant BRAFi PLX4720 (an analog of the FDA-approved drug vemurafenib) inhibited melanoma cell proliferation to a greater extent than either treatment alone. This occurred in vitro in multiple mutant BRAF cell lines and in a novel patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model system. Mechanistically, the combination increased DNA damage accumulation, which correlated with a global decrease in DNA damage repair (DDR) gene expression and increased apoptotic markers. After discontinuing PLX4720 treatment, cells showed marked recurrence. However, knockdown of RRM2 attenuated this rebound growth both in vitro and in vivo, which correlated with maintenance of the senescence-associated cell-cycle arrest.
Implications: Inhibition of RRM2 converts the transient response of melanoma cells to BRAFi to a stable response and may be a novel combinatorial strategy to prolong therapeutic response of patients with melanoma. Mol Cancer Res; 14(9); 767-75. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of Interest: None to report
Figures
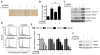

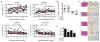

Similar articles
-
Phase I Dose-Escalation and -Expansion Study of the BRAF Inhibitor Encorafenib (LGX818) in Metastatic BRAF-Mutant Melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 15;23(18):5339-5348. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2923. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28611198 Clinical Trial.
-
BET and BRAF inhibitors act synergistically against BRAF-mutant melanoma.Cancer Med. 2016 Jun;5(6):1183-93. doi: 10.1002/cam4.667. Epub 2016 May 11. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27169980 Free PMC article.
-
A Nexus Consisting of Beta-Catenin and Stat3 Attenuates BRAF Inhibitor Efficacy and Mediates Acquired Resistance to Vemurafenib.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jun;8:132-149. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.037. Epub 2016 May 1. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27428425 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF as a target for cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Mar;11(3):285-95. doi: 10.2174/187152011795347469. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21426297 Review.
-
Cancer Fighting SiRNA-RRM2 Loaded Nanorobots.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020;8(2):79-90. doi: 10.2174/2211738508666200128120142. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32003677 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of RRM2 as an independent predictive factor of poor prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 19;13(3):3518-3535. doi: 10.18632/aging.202292. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33411689 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of subgroups along the glycolysis-cholesterol synthesis axis and the development of an associated prognostic risk model.Hum Genomics. 2021 Aug 12;15(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40246-021-00350-3. Hum Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34384498 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potential Biomarkers in Glioblastoma through Bioinformatic Analysis and Evaluating Their Prognostic Value.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 15;2019:6581576. doi: 10.1155/2019/6581576. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31119182 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of cyclin F mRNA expression in the survival of skin melanoma patients: Comprehensive analysis of the pathways altered due to cyclin F upregulation.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jul;40(1):123-144. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6435. Epub 2018 May 16. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29767233 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis revealing prognostic significance of RRM2 gene in breast cancer.Biosci Rep. 2019 Apr 9;39(4):BSR20182062. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182062. Print 2019 Apr 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30898978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Karaszewska B, Schachter J, Rutkowski P, Mackiewicz A, Stroiakovski D, et al. Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:30–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

