Atrial fibrillation without comorbidities: Prevalence, incidence and prognosis (from the Framingham Heart Study)
- PMID: 27297859
- PMCID: PMC4908973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.03.023
Atrial fibrillation without comorbidities: Prevalence, incidence and prognosis (from the Framingham Heart Study)
Abstract
Background: The epidemiology of atrial fibrillation (AF) without comorbidities, known as 'lone AF', is uncertain. Although it has been considered a benign condition, we hypothesized that it confers a worse prognosis compared with a matched sample without AF.
Methods: We described the proportion of AF without comorbidities (clinical, subclinical cardiovascular disease and triggers) among the entire AF sample in Framingham Heart Study (FHS). We compared AF without comorbidities with typical AF, and age-, sex- and cohort-matched individuals without AF, using Cox proportional hazards analysis in relation to combined cardiovascular events (stroke, heart failure, myocardial infarction), and mortality.
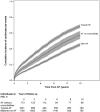
Results: Of 10,311 FHS participants, 1,961 were diagnosed with incident AF, among which 173 individuals had AF without comorbidities (47% women, mean age 71±12 years). AF without comorbidities had a prevalence of 1.7% of the entire cohort, and an annual incidence of 0.5 per 1000 person-years. During a median follow-up of 9.7 years after initial AF, 137 individuals with AF without comorbidities (79.2%) died and 141 individuals developed cardiovascular events (81.5%). AF without comorbidities had significantly lower mortality (HR 0.67, 95%CI 0.55-0.81, P < .001) and total cardiovascular events (HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.55-0.80, P < .001) compared with typical AF. However, mortality (HR1.43, 95% CI 1.18-1.75, P < .001) and risk of total cardiovascular events (HR 1.73, 95% CI 1.39-2.16, P < .001) were higher than age-, sex-, and cohort-matched individuals without AF.
Conclusions: The risk of cardiovascular outcomes and mortality among individuals with AF without comorbidities is lower than typical AF, but is significantly elevated compared with matched individuals without AF.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Potpara TS, Lip GY. Lone atrial fibrillation - an overview. Int J Clin Pract. 2014;68(4):418–33. - PubMed
-
- Kopecky SL, Gersh BJ, Mcgoon MD, et al. The Natural-History of Lone Atrial-Fibrillation - a Population-Based Study over 3 Decades. New England Journal of Medicine. 1987;317(11):669–674. - PubMed
-
- Scardi S, Mazzone C, Pandullo C, et al. Lone atrial fibrillation: prognostic differences between paroxysmal and chronic forms after 10 years of follow-up. Am Heart J. 1999;137(4 Pt 1):686–91. - PubMed
-
- Brand FN, Abbott RD, Kannel WB, et al. Characteristics and prognosis of lone atrial fibrillation. 30-year follow-up in the Framingham Study. JAMA. 1985;254(24):3449–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2015084/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- RC1 HL101056/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001453/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 2014105/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- KL2 RR031981/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R15 HL121761/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

