Beneficial therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and/or Zingiber officinale in HCV patients in Egypt
- PMID: 27298610
- PMCID: PMC4904745
Beneficial therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and/or Zingiber officinale in HCV patients in Egypt
Abstract
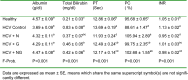
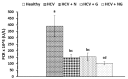
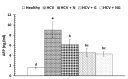
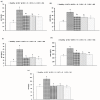
Hepatitis C is a major global health burden and Egypt has the highest prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) worldwide. The current study was designed to evaluate the beneficial therapeutic effects of ethanolic extracts of Nigella sativa, Zingiber officinale and their mixture in Egyptian HCV patients. Sixty volunteer patients with proven HCV and fifteen age matched healthy subjects were included in this study. Exclusion criteria included patients on interferon alpha (IFN-α) therapy, infection with hepatitis B virus, drug-induced liver diseases, advanced cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or other malignancies, blood picture abnormalities and major severe illness. Liver function enzymes, albumin, total bilirubin, prothrombin time and concentration, international normalized ratio, alpha fetoprotein and viral load were all assessed at baseline and at the end of the study. Ethanolic extracts of Nigella sativa and Zingiber officinale were prepared and formulated into gelatinous capsules, each containing 500 mg of Nigella sativa and/or Zingiber officinale. Clinical response and incidence of adverse drug reactions were assessed initially, periodically, and at the end of the study. Both extracts as well as their mixture significantly ameliorated the altered viral load, alpha fetoprotein, liver function parameters; with more potent effect for the combined therapy. In conclusion, administration of Nigella sativa and/or Zingiber officinale ethanolic extracts to HCV patients exhibited potential therapeutic benefits via decreasing viral load and alleviating the altered liver function, with more potent effect offered by the mixture.
Keywords: Hepatitis C; Nigella sativa; Zingiber officinale; viral load.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Gaby AM. Amino acid composition and biological effects of supplementing broad bean and corn proteins with Nigella sativa (black cumin) cake protein. Nahrung. 1998;42:290–294. - PubMed
-
- Ali BH, Blunden G. Pharmacological and toxicological properties of Nigella sativa. Phytother Res. 2003;17:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO, Nemmar A. Some phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): a review of recent research. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:409–20. - PubMed
-
- Al-Naggar TB, Gómez-Serranillos MP, Carretero ME, Villar AM. Neuropharmacological activity of Nigella sativa L. extracts. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;88:63–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
