Construction of Gene Regulatory Networks Using Recurrent Neural Networks and Swarm Intelligence
- PMID: 27298752
- PMCID: PMC4889854
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1060843
Construction of Gene Regulatory Networks Using Recurrent Neural Networks and Swarm Intelligence
Abstract
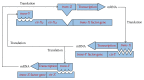
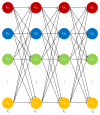
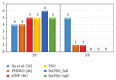
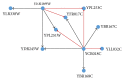
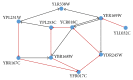
We have proposed a methodology for the reverse engineering of biologically plausible gene regulatory networks from temporal genetic expression data. We have used established information and the fundamental mathematical theory for this purpose. We have employed the Recurrent Neural Network formalism to extract the underlying dynamics present in the time series expression data accurately. We have introduced a new hybrid swarm intelligence framework for the accurate training of the model parameters. The proposed methodology has been first applied to a small artificial network, and the results obtained suggest that it can produce the best results available in the contemporary literature, to the best of our knowledge. Subsequently, we have implemented our proposed framework on experimental (in vivo) datasets. Finally, we have investigated two medium sized genetic networks (in silico) extracted from GeneNetWeaver, to understand how the proposed algorithm scales up with network size. Additionally, we have implemented our proposed algorithm with half the number of time points. The results indicate that a reduction of 50% in the number of time points does not have an effect on the accuracy of the proposed methodology significantly, with a maximum of just over 15% deterioration in the worst case.
Figures




References
-
- McLachlan G. J., Do K.-A., Ambroise C. Analyzing Microarray Gene Expression Data. Vol. 422. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 2005. - DOI
-
- D'haeseleer P., Wen X., Fuhrman S., Somogyi R. Linear modelling of mRNA expression levels during CNS development and injury. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing; 1999; pp. 41–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

