Post-traumatic Median Nerve Neuroma in Wrist. A Case Report and brief review of Literature
- PMID: 27298917
- PMCID: PMC4719255
- DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.114
Post-traumatic Median Nerve Neuroma in Wrist. A Case Report and brief review of Literature
Abstract
Introduction: Distal median nerve masses may be developed post-traumatic or non-traumatic. In this paper, we aim to present a 52 year old female case with a postraumatic neuroma of the median nerve in the left wrist.
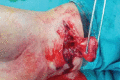
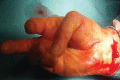
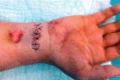
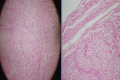
Case series: A 52-year-old female patient had accidental incised wound over her left wrist which was primarily sutured. She presented 6 months later with unrelieved pain and growing swelling at the wrist. USG showed solid mass of size 2x3 cms. Intraoperatively the mass was seen to arise from medial nerve and careful excision was done protecting the nerve. At one year follow up the patient is relived of her symptoms with no sensorimotor deficit.
Conclusion: Post traumatic neuroma present as unrelieved pain and progressive swelling. A high index of suspicion should be kept in cases of wound that are primarily sutured over an area with superficial nerves. Careful excision of the lesion is very effective in relieving patients symptoms.
Keywords: Neuroma; median nerve; nerve injury; wrist.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Figures
References
-
- Sookur PA, Saifuddin A. Indeterminate soft-tissue tumors of the hand and wrist: a review based on a clinical series of 39 cases. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40(8):977–89. - PubMed
-
- Plate AM, Lee SJ, Steiner G, Posner MA. Tumorlike lesions and benign tumors of the hand and wrist. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(2):129–41. - PubMed
-
- Kang HJ, Shin SJ, Kang ES. Schwannomas of the upper extremity. J Hand Surg Br. 2000;25(6):604–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen KH, Lee KF, Hsu HC, Huang WC, Hsiao KY, Fang KM. The role of high-resolution ultrasound in the diagnosis of a traumatic neuroma in an injured median nerve. Am JPhys Med Rehabil. 2009;88(9):771–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources