Cellular Phone Overuse as A Cause for Trapeziometacarpal Osteoarthritis: A Two Case Report
- PMID: 27298990
- PMCID: PMC4719275
- DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.213
Cellular Phone Overuse as A Cause for Trapeziometacarpal Osteoarthritis: A Two Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: New technologies have been related to upper limb diseases Trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis in young patients has not been described yet as one of these "overuse pathologies".
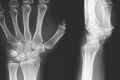
Case report: We present two cases. A 33 and a 32 year-old women, right handed, suffering from trapeziometacarpal pain. Neither previous trauma nor rheumatic disease was reported. Excessive use of last generation cellular phone was the only background reported. Pain and joint crepitation were found on physical examination and osteoarthritis signs were seen on MRI scans. One of the patients improved after using a cast, physical activity restrictions and a specific rehabilitation program; whilst the other required a corticosteroid joint injection.
Conclusion: We warn about the potential growth of these pathologies caused by an indiscriminate use (or abuse) of touch-screen cellular phones.
Keywords: Cellular phone; Hand; Osteoarthritis; Trapeziometacarpal joint.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Figures
References
-
- Hakala PT, Rimpelä AH, Saarni LA, Salminen JJ. Frequent computer-related activities increase the risk of neck-shoulder and low back pain in adolescents. Eur J Public Health. 2006 Oct;16(5):536–41. - PubMed
-
- Mirman MJ, Bonian VG. ‘Mouse elbow’: a new repetitive stress injury. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1992 Jun;92(6):701. - PubMed
-
- Yoong JK. Mobile phones can be a pain-text messaging tenosynovitis. Hosp Med. 2005 Jun;66(6):370. - PubMed
-
- Storr EF, de Vere Beavis FO, Stringer MD. Texting tenosynovitis. N Z Med J. 2007 Dec 14;120(1267):U2868. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous