Screening Utility of the King-Devick Test in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease Dementia
- PMID: 27299935
- PMCID: PMC5154783
- DOI: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000157
Screening Utility of the King-Devick Test in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease Dementia
Abstract
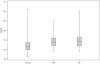
The King-Devick (K-D) test is a 1 to 2 minute, rapid number naming test, often used to assist with detection of concussion, but also has clinical utility in other neurological conditions (eg, Parkinson disease). The K-D involves saccadic eye and other eye movements, and abnormalities thereof may be an early indicator of Alzheimer disease (AD)-associated cognitive impairment. No study has tested the utility of the K-D in AD and we sought to do so. The sample included 206 [135 controls, 39 mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and 32 AD dementia] consecutive subjects from the Boston University Alzheimer's Disease Center registry undergoing their initial annual evaluation between March 2013 and July 2015. The K-D was administered during this period. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves generated from logistic regression models revealed the K-D test distinguished controls from subjects with cognitive impairment (MCI and AD dementia) [area under the curve (AUC)=0.72], MCI (AUC=0.71) and AD dementia (AUC=0.74). K-D time scores between 48 and 52 seconds were associated with high sensitivity (>90.0%) and negative predictive values (>85.0%) for each diagnostic group. The K-D correlated strongly with validated attention, processing speed, and visual scanning tests. The K-D test may be a rapid and simple effective screening tool to detect cognitive impairment associated with AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. 2015 Available at: http://www.alz.org/facts/. Accessed December 7, 2015.
-
- Connolly A, Gaehl E, Martin H, et al. Underdiagnosis of dementia in primary care: variations in the observed prevalence and comparisons to the expected prevalence. Aging Ment Health. 2011;15:978–984. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical