YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer
- PMID: 27300434
- PMCID: PMC6186419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.005
YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer
Abstract
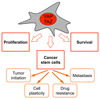
YAP and TAZ are highly related transcriptional regulators pervasively activated in human malignancies. Recent work indicates that, remarkably, YAP/TAZ are essential for cancer initiation or growth of most solid tumors. Their activation induces cancer stem cell attributes, proliferation, chemoresistance, and metastasis. YAP/TAZ are sensors of the structural and mechanical features of the cell microenvironment. A number of cancer-associated extrinsic and intrinsic cues conspire to overrule the YAP-inhibiting microenvironment of normal tissues, including changes in mechanotransduction, inflammation, oncogenic signaling, and regulation of the Hippo pathway. Addiction to YAP/TAZ thus potentially represents a central cancer vulnerability that may be exploited therapeutically.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, Piccolo S. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell. 2013;154:1047–1059. - PubMed
-
- Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E, Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V, et al. YAP/TAZ incorporation in the beta-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell. 2014;158:157–170. - PubMed
-
- Azzolin L, Zanconato F, Bresolin S, Forcato M, Basso G, Bicciato S, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. Role of TAZ as mediator of Wnt signaling. Cell. 2012;151:1443–1456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

