Intra-articular injection of Torin 1 reduces degeneration of articular cartilage in a rabbit osteoarthritis model
- PMID: 27301478
- PMCID: PMC4921044
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.56.BJR-2015-0001
Intra-articular injection of Torin 1 reduces degeneration of articular cartilage in a rabbit osteoarthritis model
Abstract
Objectives: Recent studies have shown that systemic injection of rapamycin can prevent the development of osteoarthritis (OA)-like changes in human chondrocytes and reduce the severity of experimental OA. However, the systemic injection of rapamycin leads to many side effects. The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of intra-articular injection of Torin 1, which as a specific inhibitor of mTOR which can cause induction of autophagy, is similar to rapamycin, on articular cartilage degeneration in a rabbit osteoarthritis model and to investigate the mechanism of Torin 1's effects on experimental OA.
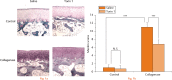
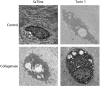
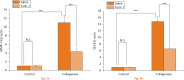
Methods: Collagenase (type II) was injected twice into both knees of three-month-old rabbits to induce OA, combined with two intra-articular injections of Torin 1 (400 nM). Degeneration of articular cartilage was evaluated by histology using the Mankin scoring system at eight weeks after injection. Chondrocyte degeneration and autophagosomes were observed by transmission electron microscopy. Matrix metallopeptidase-13 (MMP-13) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression were analysed by quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR).Beclin-1 and light chain 3 (LC3) expression were examined by Western blotting.
Results: Intra-articular injection of Torin 1 significantly reduced degeneration of the articular cartilage after induction of OA. Autophagosomes andBeclin-1 and LC3 expression were increased in the chondrocytes from Torin 1-treated rabbits. Torin 1 treatment also reduced MMP-13 and VEGF expression at eight weeks after collagenase injection.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that intra-articular injection of Torin 1 reduces degeneration of articular cartilage in collagenase-induced OA, at least partially by autophagy activation, suggesting a novel therapeutic approach for preventing cartilage degeneration and treating OA.Cite this article: N-T. Cheng, A. Guo, Y-P. Cui. Intra-articular injection of Torin 1 reduces degeneration of articular cartilage in a rabbit osteoarthritis model. Bone Joint Res 2016;5:218-224. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.56.BJR-2015-0001.
Keywords: Articular cartilage degradation; Autophagy; Intra-articular injection; Osteoarthritis; Torin 1.
© 2016 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intra-articular Injection of Chloramphenicol Reduces Articular Cartilage Degeneration in a Rabbit Model of Osteoarthritis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Dec;477(12):2785-2797. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001016. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31764352 Free PMC article.
-
Local intra-articular injection of rapamycin delays articular cartilage degeneration in a murine model of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Nov 17;16(6):482. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0482-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25403236 Free PMC article.
-
The protective role of autophagy in experimental osteoarthritis, and the therapeutic effects of Torin 1 on osteoarthritis by activating autophagy.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Apr 6;17:150. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-0995-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27052304 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in osteoarthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2016 Mar;83(2):143-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Joint Bone Spine. 2016. PMID: 26453105 Review.
-
Intra-articular nanodrug delivery strategies for treating osteoarthritis.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Mar;28(3):103482. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.103482. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 36584875 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy Is Independent of the Chondroprotection Induced by Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jul 24;2018:9726703. doi: 10.1155/2018/9726703. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30140705 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Novel Avenues in mTOR-Targeted Therapeutics: Advancements in Glioblastoma Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14960. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914960. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of mTORC1 by rapamycin results in feedback activation of AktS473 and aggravates hallmarks of osteoarthritis in female mice and non-human primates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 6:2024.05.14.594256. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.14.594256. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 38798488 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Intraperitoneal injection of the SIRT1 activator SRT1720 attenuates the progression of experimental osteoarthritis in mice.Bone Joint Res. 2018 May 5;7(3):252-262. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.73.BJR-2017-0227.R1. eCollection 2018 Mar. Bone Joint Res. 2018. PMID: 29922443 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of alendronate on cartilage lesions and micro-architecture deterioration of subchondral bone in patellofemoral osteoarthritic ovariectomized rats with patella-baja.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Mar 25;19(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04677-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38528611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lahm A, Kasch R, Mrosek E, et al. Semiquantitative analysis of ECM molecules in the different cartilage layers in early and advanced osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Histol Histopathol 2012;27:609-615. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg HM. Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 2003;423:332-336. - PubMed
-
- Urbanek T, Kuczmik W, Basta-Kaim A, Gabryel B. Rapamycin induces of protective autophagy in vascular endothelial cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Brain Res 2014;1553:1-11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

