Crizotinib in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma in the setting of renal insufficiency: a case report
- PMID: 27301488
- PMCID: PMC4908805
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-016-0963-y
Crizotinib in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma in the setting of renal insufficiency: a case report
Abstract
Background: In vitro studies confirmed cytoreductive anti-tumor activity of crizotinib in experimental models of anaplastic large cell lymphoma in 2007. One case series and a few case reports describe the use of crizotinib in relapsed or refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Even though data are limited regarding the dose of crizotinib in renal insufficiency, our case was successfully treated with a lower dose of crizotinib.
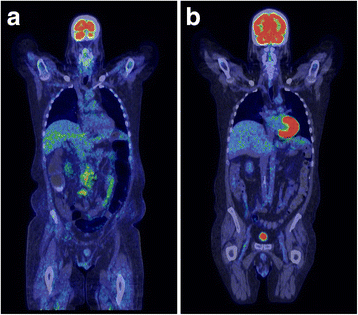
Case presentation: We report the case of a 48-year-old white man who had progressive disease after three prior cycles of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone and three cycles of ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide, and was not a candidate for high-dose chemotherapy and transplant due to poor performance status and renal insufficiency; he had a complete and durable response to single agent crizotinib. Crizotinib was given at a reduced dose (250 mg once daily) due to his renal insufficiency. He has been in complete remission for more than 2 years.
Conclusions: Our experience confirms the activity of crizotinib in this disease; it suggests that long-term treatment with crizotinib is a reasonable option in patients who are not candidates for more aggressive therapy and indicates that crizotinib can be used successfully at reduced doses in patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency. The role and timing of crizotinib in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma is unclear, but the current literature that we review here provides promising results that may lead to studies of crizotinib earlier in the course of disease.
Keywords: ALK; Anaplastic large cell lymphoma; Crizotinib; Renal insufficiency.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ALK expression plays different roles in anaplastic large-cell lymphomas and outcome of crizotinib use in relapsed/refractory ALK+ patients in a Chinese population.Ann Hematol. 2018 Jan;97(1):149-159. doi: 10.1007/s00277-017-3166-8. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Ann Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29150811
-
Crizotinib in Combination with Everolimus Synergistically Inhibits Proliferation of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase‒Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma.Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Apr;50(2):599-613. doi: 10.4143/crt.2016.357. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 28675026 Free PMC article.
-
Brentuximab vedotin and crizotinib in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma.Cancer J. 2012 Sep-Oct;18(5):450-6. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e31826aef4a. Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 23006951 Review.
-
Crizotinib as salvage and maintenance with allogeneic stem cell transplantation for refractory anaplastic large cell lymphoma.J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014 Mar 1;12(3):323-6; quiz 326. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2014.0034. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014. PMID: 24616538
-
Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of systemic anaplastic large cell lymphomas.Br J Haematol. 2015 Mar;168(6):771-83. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13265. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25559471 Review.
Cited by
-
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: pathology, genetics, and clinical aspects.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2017;57(3):120-142. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.17023. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2017. PMID: 29279550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stein H, Foss HD, Durkop H, Marafioti T, Delsol G, Pulford K, et al. CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood. 2000;96(12):3681–95. - PubMed
-
- Savage KJ, Harris NL, Vose JM, Ullrich F, Jaffe ES, Connors JM, et al. ALK-anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is clinically and immunophenotypically different from both ALK+ ALCL and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: report from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood. 2008;111(12):5496–504. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-134270. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources