Methotrexate efficacy, but not its intolerance, is associated with the dose and route of administration
- PMID: 27301536
- PMCID: PMC4908704
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-016-0099-z
Methotrexate efficacy, but not its intolerance, is associated with the dose and route of administration
Abstract
Background: There is a lack of published evidence on the importance of methotrexate (MTX) dose and route of administration on both its efficacy and adverse events in children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA). We aimed to document our clinical practice based on the treat-to-target approach in order to support the concept that better therapeutic effect achieved with an optimal dose of parenteral MTX is associated with clinically acceptable adverse effects comparable to those reported for oral treatment.
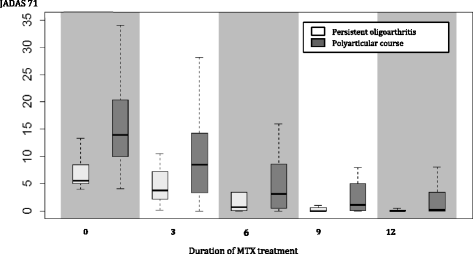
Methods: Study inclusion criteria were indication of new MTX therapy for active arthritis in confirmed JIA patients younger than 18 years. Eligible patients were evaluated prospectively every 3 months for 1 year using standardized instruments for treatment response (American College of Rheumatology Pediatric (ACRPedi) response, Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score (JADAS) 71, Clinically Inactive Disease (CID)) and adverse events (laboratory monitoring, Methotrexate Intolerance Severity Score (MISS)). MTX responders had to achieve at least ACRPedi 70 response. MTX intolerance was defined by MISS ≥ 6.
Results: In 45/55 patients (81.8 %) MTX was started as subcutaneous injection. The initial median weekly dose was 14.4 mg/m(2) in parenteral and 11.7 mg/m(2) in oral administration. MTX therapy was effective in the level of ACRpedi70 and CID in 50.9 % and 30.9 % of patients at month 6 and in 70.9 % and 56.4 % after 12 months of the treatment, respectively. MTX intolerance at 6 and 12 months was noted in 25.5 % and 30.6 %, respectively. Management of intolerance included change in the dose and/or route of administration, education and councelling. Adverse events led to MTX withdrawal in 5 patients (9 %) due to toxicity (n = 3) and intolerance (n = 2). We did not find any significant predictive factors for either MTX therapeutic response or intolerance.
Conclusion: Subcutaneous MTX weekly dose around 15 mg/m(2) is associated not only with a high response rate within the first 12 months of treatment, but also with a relatively low rate of significant adverse effects that would lead to the treatment termination. It allows early recognition of MTX non-responders and addition of biologic therapy. Sustainability of therapeutic effect and longer-term evolution of adverse events will be addressed by an ongoing extension of the study.
Keywords: Efficacy; Intolerance; Juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Methotrexate; Quality of life; Toxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methotrexate intolerance in oral and subcutaneous administration in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a cross-sectional, observational study.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Jan-Feb;34(1):148-54. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26843067
-
A comparison of three treatment strategies in recent onset non-systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: initial 3-months results of the BeSt for Kids-study.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2017 Feb 6;15(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12969-017-0138-4. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2017. PMID: 28166785 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intolerance of oral methotrexate in juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Pediatr Int. 2025 Jan-Dec;67(1):e70112. doi: 10.1111/ped.70112. Pediatr Int. 2025. PMID: 40539404
-
Methotrexate-induced nausea in the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2017 Jun 19;15(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12969-017-0180-2. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2017. PMID: 28629458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methotrexate and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Evidence Regarding Subcutaneous Versus Oral Routes of Administration.Adv Ther. 2016 Mar;33(3):369-78. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0295-8. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Adv Ther. 2016. PMID: 26846283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ABCC1, ABCG2 and FOXP3: Predictive Biomarkers of Toxicity from Methotrexate Treatment in Patients Diagnosed with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 19;11(9):2567. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092567. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761008 Free PMC article.
-
Oral or Parenteral Methotrexate for the Treatment of Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Eur J Rheumatol. 2022 Oct;9(4):197-205. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2022.21090. Eur J Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35943454 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Versus Subcutaneous Methotrexate in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disorders: an Update of the Current Literature.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2023 Dec;25(12):276-284. doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01116-7. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37768405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methotrexate Intolerance in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Definition, Risks, and Management.Paediatr Drugs. 2024 Sep;26(5):479-498. doi: 10.1007/s40272-024-00643-9. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Paediatr Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39044097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early and Accurate Prediction of Clinical Response to Methotrexate Treatment in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Using Machine Learning.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 7;10:1155. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01155. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31649533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beukelman T, Patkar NM, Saag KG, Tolleson-Rinehart S, Cron RQ, DeWitt EM, et al. 2011 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: initiation and safety monitoring of therapeutic agents for the treatment of arthritis and systemic features. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011;63(4):465–82. doi: 10.1002/acr.20460. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ringold S, Weiss PF, Beukelman T, DeWitt EM, Ilowite NT, Kimura Y, et al. 2013 Update of the 2011 American College of Rheumatology Recommendations for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Recommendations for the Medical Therapy of Children With Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Tuberculosis Screening Among Children Receiving Biologic Medications. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(10):2499–512. doi: 10.1002/art.38092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical