IGF-1 protects tubular epithelial cells during injury via activation of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 27301852
- PMCID: PMC4908659
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28066
IGF-1 protects tubular epithelial cells during injury via activation of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
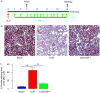
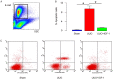
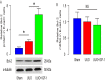
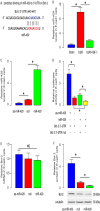
Injury of renal tubular epithelial cells can induce acute renal failure and obstructive nephropathy. Previous studies have shown that administration of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) ameliorates the renal injury in a mouse unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) model, whereas the underlying mechanisms are not completely understood. Here, we addressed this question. We found that the administration of IGF-1 significantly reduced the severity of the renal fibrosis in UUO. By analyzing purified renal epithelial cells, we found that IGF-1 significantly reduced the apoptotic cell death of renal epithelial cells, seemingly through upregulation of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, at protein but not mRNA level. Bioinformatics analyses and luciferase-reporter assay showed that miR-429 targeted the 3'-UTR of Bcl-2 mRNA to inhibit its protein translation in renal epithelial cells. Moreover, IGF-1 suppressed miR-429 to increase Bcl-2 in renal epithelial cells to improve survival after UUO. Furthermore, inhibition of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in renal epithelial cells abolished the suppressive effects of IGF-1 on miR-429 activation, and then the enhanced effects on Bcl-2 in UUO. Thus, our data suggest that IGF-1 may protect renal tubular epithelial cells via activation of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway during renal injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ulinastatin inhibits renal tubular epithelial apoptosis and interstitial fibrosis in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):8916-8922. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7692. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28990075 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanism of action of miR-483-3p in mediating the effects of IGF-1 on human renal tubular epithelial cells induced by high glucose.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 7;14(1):15635. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66433-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38972889 Free PMC article.
-
The TGFβ-ERK pathway contributes to Notch3 upregulation in the renal tubular epithelial cells of patients with obstructive nephropathy.Cell Signal. 2018 Nov;51:139-151. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30081092
-
Renal tubular cell death and inflammation response are regulated by the MAPK-ERK-CREB signaling pathway under hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019 Oct-Dec;39(5-6):383-391. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2019.1698050. Epub 2019 Nov 29. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019. PMID: 31782334 Review.
-
Tubular apoptosis in the pathophysiology of renal disease.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2002 Aug 30;114(15-16):671-7. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2002. PMID: 12602110 Review.
Cited by
-
IGF-1 protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting αSMA.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 9;12(7):688. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03965-5. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34244467 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF, proBDNF and IGF-1 serum levels in naïve and medicated subjects with autism.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13768. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17503-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35962006 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Regulatory Effect of Hydroxytyrosol on Ovarian Inflammaging Through Autophagy-Targeted Mechanisms: A Bioinformatics Approach.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 23;17(9):1421. doi: 10.3390/nu17091421. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362730 Free PMC article.
-
Renal chymase-dependent pathway for angiotensin II formation mediated acute kidney injury in a mouse model of aristolochic acid I-induced acute nephropathy.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 11;14(1):e0210656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210656. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30633770 Free PMC article.
-
An atlas of healthy and injured cell states and niches in the human kidney.Nature. 2023 Jul;619(7970):585-594. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05769-3. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37468583 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

