Global re-wiring of p53 transcription regulation by the hepatitis B virus X protein
- PMID: 27302019
- PMCID: PMC5423203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.05.006
Global re-wiring of p53 transcription regulation by the hepatitis B virus X protein
Abstract
Background: The tumour suppressor p53 is a central player in transcription regulation and cell fate determination. By interacting with p53 and altering its sequence-specific binding to the response elements, the hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) was reported to re-direct p53 regulation of some genes.
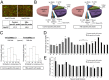
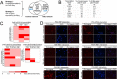
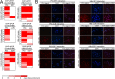
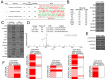
Results: Coupling massively parallel deep sequencing with p53 chromatin immunoprecipitation, we demonstrate that HBx modulates global p53 site selection and that this was strongly influenced by altered interaction with transcription co-factors/co-regulators as well as post-translational modifications. Specifically, HBx attenuated p53-TBP-RB1 transcription complex recruitment and interaction and this was associated with hyper-phosphorylation of p53 at serine 315 by HBx. Concurrently, HBx enhanced p53 DNA occupancy to other response elements either alone by displacing specific transcription factors such as CEBPB and NFkB1, or in complex with distinct interacting co-factors Sp1, JUN and E2F1. Importantly, re-wiring of p53 transcription regulation by HBx was linked to the deregulation of genes involved in cell proliferation and death, suggesting a role of HBx in errant cell fate determination mediated by altered p53 site selection of target genes.
Conclusions: Our study thus presents first evidence of global modes of p53 transcription alteration by HBx and provides new insights to understand and potentially curtail the viral oncoprotein.
Keywords: ChIP-Seq; HBx; P53 transcription; Phosphorylation; p53 serine 315.
Copyright © 2016 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered binding site selection of p53 transcription cassettes by hepatitis B virus X protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;33(3):485-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01189-12. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23149944 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B viral transactivator HBx alleviates p53-mediated repression of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 8;275(36):27806-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004449200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10842185
-
Chemotherapeutic drug, adriamycin, restores the function of p53 protein in hepatitis B virus X (HBx) protein-expressing liver cells.Oncogene. 2000 Oct 26;19(45):5163-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203896. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11064453
-
Hepatitis B virus x protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jan;26 Suppl 1:144-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06546.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21199526 Review.
-
Hepatocarcinogenesis in viral Hepatitis B infection: the role of HBx and p53.Acta Med Indones. 2006 Jul-Sep;38(3):154-9. Acta Med Indones. 2006. PMID: 16953033 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor E4F1 as a regulator of cell life and disease progression.Sci Adv. 2023 Sep 29;9(39):eadh1991. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh1991. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37774036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor suppressor p53: from engaging DNA to target gene regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 18;48(16):8848-8869. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa666. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32797160 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the preventable causes of cancer in the United States.Genes Dev. 2018 Jul 1;32(13-14):868-902. doi: 10.1101/gad.314849.118. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29945886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR Signaling: The Interface Linking Cellular Metabolism and Hepatitis B Virus Replication.Virol Sin. 2021 Dec;36(6):1303-1314. doi: 10.1007/s12250-021-00450-3. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Virol Sin. 2021. PMID: 34580816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The p53 family member p73 in the regulation of cell stress response.Biol Direct. 2021 Nov 8;16(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13062-021-00307-5. Biol Direct. 2021. PMID: 34749806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chuikov, S. , Kurash, J.K. , Wilson, J.R. , Xiao, B. , Justin, N. , Ivanov, G.S. , Mckinney, K. , Tempst, P. , Prives, C. , Gamblin, S.J. , Barlev, N.A. , Reinberg, D. , 2004. Regulation of p53 activity through lysine methylation. Nature 432, 353–360. - PubMed
-
- Chung, T.W. , Lee, Y.C. , Ko, J.H. , Kim, C.H. , 2003. Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates the expression of PTEN by inhibiting the function of p53, a transcriptional activator in liver cells. Cancer Res. 63, 3453–3458. - PubMed
-
- El-Deiry, W.S. , Kern, S.E. , Pietenpol, J.A. , Kinzler, K.W. , Vogelstein, B. , 1992. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat. Genet. 1, 45–49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

