Curcumin Ameliorates Ischemia-Induced Limb Injury Through Immunomodulation
- PMID: 27302110
- PMCID: PMC4913813
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.896217
Curcumin Ameliorates Ischemia-Induced Limb Injury Through Immunomodulation
Abstract
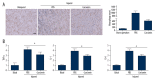
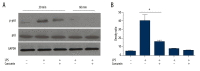
BACKGROUND The prevalence of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is increasing worldwide. Currently, there is no effective treatment for PAD. Curcumin is an ingredient of turmeric that has antioxidant, anti-inflammation, and anticancer properties. In the present study we investigated the potential effect of curcumin in protecting against ischemic limb injury. MATERIAL AND METHODS We used an established hindlimb ischemia mouse model in our study. Curcumin was administrated through intraperitoneal (I.P.) injection. Immunohistochemical staining and ELISA assays were performed. Treadmill training was used to evaluate skeletal muscle functions of animals. RESULTS Our experiments using in vivo treadmill training showed that curcumin treatment improved the running capacity of animals after ischemic injury. Histological analysis revealed that curcumin treatment significantly reduced the skeletal muscle damage and fibrosis associated with ischemic injury. In order to determine the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying curcumin-mediated tissue protection, immunohistochemical staining and ELISA assays were performed. The results showed that curcumin treatment led to less macrophage infiltration and less local inflammatory responses as demonstrated by decreasing TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 levels. Further immunofluorescent staining of tissue slides indicated that curcumin treatment inhibited the NF-κB signaling pathway. Finally, curcumin can inhibit NF-kB activation induced by LPS in macrophages. CONCLUSIONS Our study results show that curcumin treatment can ameliorate hindlimb injury following ischemic surgery, which suggests that curcumin could be used for PAD treatment.
Figures



References
-
- Aronow WS. Management of peripheral arterial disease of the lower extremities. Compr Ther. 2007;33:247–56. - PubMed
-
- Dutta S, Padhye S, Priyadarsini KI, Newton C. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of curcumin semicarbazone. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005;15:2738–44. - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Fu J, Yu M, et al. Effects of three kinds of curcuminoids on anti-oxidative system and membrane deformation of human peripheral blood erythrocytes in high glucose levels. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Lim CS, Jin DQ, Mok H, et al. Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of xanthorrhizol in hippocampal neurons and primary cultured microglia. J Neurosci Res. 2005;82:831–38. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, Khar A. Biological effects of curcumin and its role in cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006;6:259–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

