Adolescent Alcohol Exposure: Burden of Epigenetic Reprogramming, Synaptic Remodeling, and Adult Psychopathology
- PMID: 27303256
- PMCID: PMC4885838
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00222
Adolescent Alcohol Exposure: Burden of Epigenetic Reprogramming, Synaptic Remodeling, and Adult Psychopathology
Abstract
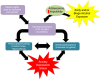
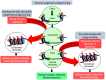
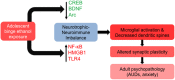
Adolescence represents a crucial phase of synaptic maturation characterized by molecular changes in the developing brain that shape normal behavioral patterns. Epigenetic mechanisms play an important role in these neuromaturation processes. Perturbations of normal epigenetic programming during adolescence by ethanol can disrupt these molecular events, leading to synaptic remodeling and abnormal adult behaviors. Repeated exposure to binge levels of alcohol increases the risk for alcohol use disorder (AUD) and comorbid psychopathology including anxiety in adulthood. Recent studies in the field clearly suggest that adolescent alcohol exposure causes widespread and persistent changes in epigenetic, neurotrophic, and neuroimmune pathways in the brain. These changes are manifested by altered synaptic remodeling and neurogenesis in key brain regions leading to adult psychopathology such as anxiety and alcoholism. This review details the molecular mechanisms underlying adolescent alcohol exposure-induced changes in synaptic plasticity and the development of alcohol addiction-related phenotypes in adulthood.
Keywords: adolescence; anxiety; binge drinking; dendritic spines; epigenetics; neurogenesis; neuroinflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Alaux-Cantin S., Warnault V., Legastelois R., Botia B., Pierrefiche O., Vilpoux C., et al. . (2013). Alcohol intoxications during adolescence increase motivation for alcohol in adult rats and induce neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 67, 521–531. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.12.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balosso S., Liu J., Bianchi M. E., Vezzani A. (2014). Disulfide-containing high mobility group box-1 promotes N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function and excitotoxicity by activating Toll-like receptor 4-dependent signaling in hippocampal neurons. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 21, 1726–1740. 10.1089/ars.2013.5349 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

