Ribosomal Protein Rps26 Influences 80S Ribosome Assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 27303706
- PMCID: PMC4863615
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00109-15
Ribosomal Protein Rps26 Influences 80S Ribosome Assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
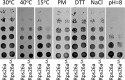
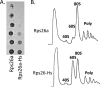
The eukaryotic ribosome consists of a small (40S) and a large (60S) subunit. Rps26 is one of the essential ribosomal proteins of the 40S subunit and is encoded by two almost identical genes, RPS26a and RPS26b. Previous studies demonstrated that Rps26 interacts with the 5' untranslated region of mRNA via the eukaryote-specific 62-YXXPKXYXK-70 (Y62-K70) motif. Those observations suggested that this peptide within Rps26 might play an important and specific role during translation initiation. By using alanine-scanning mutagenesis and engineered strains of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we found that single amino acid substitutions within the Y62-K70 motif of Rps26 did not affect the in vivo function of the protein. In contrast, complete deletion of the Y62-K70 segment was lethal. The simultaneous replacement of five conserved residues within the Y62-K70 segment by alanines resulted in growth defects under stress conditions and produced distinct changes in polysome profiles that were indicative of the accumulation of free 60S subunits. Human Rps26 (Rps26-Hs), which displays significant homology with yeast Rps26, supported the growth of an S. cerevisiae Δrps26a Δrps26b strain. However, the Δrps26a Δrps26b double deletion strain expressing Rps26-Hs displayed substantial growth defects and an altered ratio of 40S/60S ribosomal subunits. The combined data strongly suggest that the eukaryote-specific motif within Rps26 does not play a specific role in translation initiation. Rather, the data indicate that Rps26 as a whole is necessary for proper assembly of the 40S subunit and the 80S ribosome in yeast. IMPORTANCE Rps26 is an essential protein of the eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit. Previous experiments demonstrated an interaction between the eukaryote-specific Y62-K70 segment of Rps26 and the 5' untranslated region of mRNA. The data suggested a specific role of the Y62-K70 motif during translation initiation. Here, we report that single-site substitutions within the Y62-K70 peptide did not affect the growth of engineered yeast strains, arguing against its having a critical role during translation initiation via specific interactions with the 5' untranslated region of mRNA molecules. Only the simultaneous replacement of five conserved residues within the Y62-K70 fragment or the replacement of the yeast protein with the human homolog resulted in growth defects and caused significant changes in polysome profiles. The results expand our knowledge of ribosomal protein function and suggest a role of Rps26 during ribosome assembly in yeast.
Keywords: 40S subunit; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; eukaryote-specific motif; mutagenesis; ribosomal protein; ribosome assembly; translation initiation; yeast genetics.
Figures



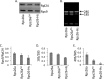
Similar articles
-
FLO11 mediated filamentous growth of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on the expression of the ribosomal RPS26 genes.Mol Genet Genomics. 2006 Aug;276(2):113-25. doi: 10.1007/s00438-006-0127-7. Epub 2006 May 24. Mol Genet Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16721598
-
PsRPs26, a 40S Ribosomal Protein Subunit, Regulates the Growth and Pathogenicity of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici.Front Microbiol. 2019 May 10;10:968. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00968. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31134016 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrapeptide 60-63 of human ribosomal protein uS3 is crucial for translation initiation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Sep;1862(9):194411. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.194411. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 31356988
-
In vivo deletion analysis of the architecture of a multiprotein complex of translation initiation factors.Methods Enzymol. 2007;431:15-32. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)31002-1. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17923228 Review.
-
Eukaryote-specific extensions in ribosomal proteins of the small subunit: Structure and function.Translation (Austin). 2015 Feb 5;3(1):e999576. doi: 10.1080/21690731.2014.999576. eCollection 2015 Jan-Jun. Translation (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26779416 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Profile Alteration with Cadmium Selenide/Zinc Sulfide Quantum Dots in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biomolecules. 2019 Oct 25;9(11):653. doi: 10.3390/biom9110653. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31731522 Free PMC article.
-
Two "Edges" in Our Knowledge on the Functions of Ribosomal Proteins: The Revealed Contributions of Their Regions to Translation Mechanisms and the Issues of Their Extracellular Transport by Exosomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11458. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411458. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complementary transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal regulatory mechanisms of milk protein production in dairy cows consuming different forages.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 14;7:44234. doi: 10.1038/srep44234. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28290485 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Transcriptome Profiles of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Cells Exposed to Cadmium Selenide/Zinc Sulfide and Indium Phosphide/Zinc Sulfide.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 17;12(3):428. doi: 10.3390/genes12030428. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802854 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics Answers Which Yeast Genes Are Specific for Baking, Brewing, and Ethanol Production.Bioengineering (Basel). 2020 Nov 18;7(4):147. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering7040147. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33217975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collatz E, Ulbrich N, Tsurugi K, Lightfoot HN, MacKinlay W, Lin A, Wool IG. 1977. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of the 40-S ribosomal subunit proteins Sa, Sc, S3a, S3b, S5', S9, S10, S11, S12, S14, S15, S15', S16, S17, S18, S19, S20, S21, S26, S27', and S29. J Biol Chem 252:9071–9080. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

