DMET™ (Drug Metabolism Enzymes and Transporters): a pharmacogenomic platform for precision medicine
- PMID: 27304055
- PMCID: PMC5288240
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9927
DMET™ (Drug Metabolism Enzymes and Transporters): a pharmacogenomic platform for precision medicine
Abstract
In the era of personalized medicine, high-throughput technologies have allowed the investigation of genetic variations underlying the inter-individual variability in drug pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics. Several studies have recently moved from a candidate gene-based pharmacogenetic approach to genome-wide pharmacogenomic analyses to identify biomarkers for selection of patient-tailored therapies. In this aim, the identification of genetic variants affecting the individual drug metabolism is relevant for the definition of more active and less toxic treatments. This review focuses on the potentiality, reliability and limitations of the DMET™ (Drug Metabolism Enzymes and Transporters) Plus as pharmacogenomic drug metabolism multi-gene panel platform for selecting biomarkers in the final aim to optimize drugs use and characterize the individual genetic background.
Keywords: ADME genes; DMET™; biomarkers; pharmacogenomics; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
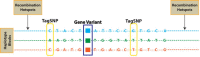


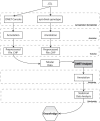


References
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, Funke R, Gage D, Harris K, Heaford A, Howland J, Kann L, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG, Smith HO, Yandell M, Evans CA, Holt RA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides P, Ballew RM, Huson DH, Wortman JR, Zhang Q, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Lin M, Aquilante C, Johnson JA, Wu R. Sequencing drug response with HapMap. The pharmacogenomics journal. 2005;5:149–156. - PubMed
-
- Evans WE, McLeod HL. Pharmacogenomics—drug disposition, drug targets, and side effects. The New England journal of medicine. 2003;348:538–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
