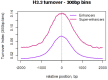
Enhancer regions show high histone H3.3 turnover that changes during differentiation
- PMID: 27304074
- PMCID: PMC4965263
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.15316
Enhancer regions show high histone H3.3 turnover that changes during differentiation
Abstract
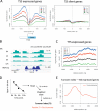
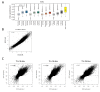
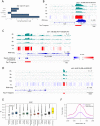
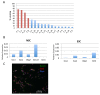
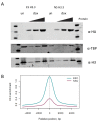
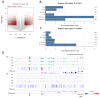
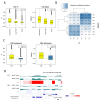
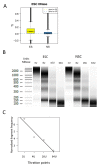
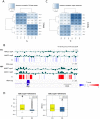
The organization of DNA into chromatin is dynamic; nucleosomes are frequently displaced to facilitate the ability of regulatory proteins to access specific DNA elements. To gain insight into nucleosome dynamics, and to follow how dynamics change during differentiation, we used a technique called time-ChIP to quantitatively assess histone H3.3 turnover genome-wide during differentiation of mouse ESCs. We found that, without prior assumptions, high turnover could be used to identify regions involved in gene regulation. High turnover was seen at enhancers, as observed previously, with particularly high turnover at super-enhancers. In contrast, regions associated with the repressive Polycomb-Group showed low turnover in ESCs. Turnover correlated with DNA accessibility. Upon differentiation, numerous changes in H3.3 turnover rates were observed, the majority of which occurred at enhancers. Thus, time-ChIP measurement of histone turnover shows that active enhancers are unusually dynamic in ESCs and changes in highly dynamic nucleosomes predominate at enhancers during differentiation.
Keywords: chromatin; chromosomes; differentiation; genes; histone H3.3; mouse; stem cells; turnover.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
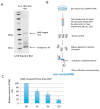
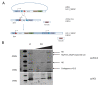
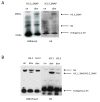
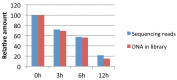
References
-
- Abubucker S, Segata N, Goll J, Schubert AM, Izard J, Cantarel BL, Rodriguez-Mueller B, Zucker J, Thiagarajan M, Henrissat B, White O, Kelley ST, Methé B, Schloss PD, Gevers D, Mitreva M, Huttenhower C. Metabolic reconstruction for metagenomic data and its application to the human microbiome. PLoS Computational Biology. 2012;8:e15316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002358. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, Jaenisch R, Wagschal A, Feil R, Schreiber SL, Lander ES. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.041. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

