Dbl2 Regulates Rad51 and DNA Joint Molecule Metabolism to Ensure Proper Meiotic Chromosome Segregation
- PMID: 27304859
- PMCID: PMC4909299
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006102
Dbl2 Regulates Rad51 and DNA Joint Molecule Metabolism to Ensure Proper Meiotic Chromosome Segregation
Abstract
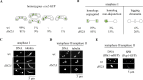
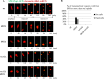
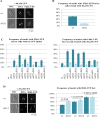
To identify new proteins required for faithful meiotic chromosome segregation, we screened a Schizosaccharomyces pombe deletion mutant library and found that deletion of the dbl2 gene led to missegregation of chromosomes during meiosis. Analyses of both live and fixed cells showed that dbl2Δ mutant cells frequently failed to segregate homologous chromosomes to opposite poles during meiosis I. Removing Rec12 (Spo11 homolog) to eliminate meiotic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) suppressed the segregation defect in dbl2Δ cells, indicating that Dbl2 acts after the initiation of meiotic recombination. Analyses of DSBs and Holliday junctions revealed no significant defect in their formation or processing in dbl2Δ mutant cells, although some Rec12-dependent DNA joint molecules persisted late in meiosis. Failure to segregate chromosomes in the absence of Dbl2 correlated with persistent Rad51 foci, and deletion of rad51 or genes encoding Rad51 mediators also suppressed the segregation defect of dbl2Δ. Formation of foci of Fbh1, an F-box helicase that efficiently dismantles Rad51-DNA filaments, was impaired in dbl2Δ cells. Our results suggest that Dbl2 is a novel regulator of Fbh1 and thereby Rad51-dependent DSB repair required for proper meiotic chromosome segregation and viable sex cell formation. The wide conservation of these proteins suggests that our results apply to many species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




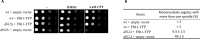
Similar articles
-
A failure of meiotic chromosome segregation in a fbh1Delta mutant correlates with persistent Rad51-DNA associations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Mar;39(5):1718-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq977. Epub 2010 Dec 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21149262 Free PMC article.
-
SCF ensures meiotic chromosome segregation through a resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030622. Epub 2012 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22292001 Free PMC article.
-
The F-Box DNA helicase Fbh1 prevents Rhp51-dependent recombination without mediator proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(18):8084-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.8084-8096.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16135800 Free PMC article.
-
Double-stranded DNA breaks and gene functions in recombination and meiosis.Cell Res. 2006 May;16(5):402-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310052. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16699536 Review.
-
Self-organization of meiotic recombination initiation: general principles and molecular pathways.Annu Rev Genet. 2014;48:187-214. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092304. Annu Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25421598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H2A insufficiency causes chromosomal segregation defects due to anaphase chromosome bridge formation at rDNA repeats in fission yeast.Sci Rep. 2019 May 9;9(1):7159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43633-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31073221 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse ZGRF1 helicase facilitates DNA repair and maintains efficient fertility.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 16;11(2):e41979. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41979. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39897830 Free PMC article.
-
CDK phosphorylation of Sfr1 downregulates Rad51 function in late-meiotic homolog invasions.EMBO J. 2024 Oct;43(19):4356-4383. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00205-2. Epub 2024 Aug 22. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39174851 Free PMC article.
-
Dbl2 interacts with helicases and an endonuclease to maintain the integrity of repetitive regions.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21895. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08626-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594858 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclins and CDKs in the regulation of meiosis-specific events.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 29;10:1069064. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1069064. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36523509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petronczki M, Siomos MF, Nasmyth K (2003) Un menage a quatre: the molecular biology of chromosome segregation in meiosis. Cell 112: 423–440. - PubMed
-
- Kudo NR, Wassmann K, Anger M, Schuh M, Wirth KG, et al. (2006) Resolution of chiasmata in oocytes requires separase-mediated proteolysis. Cell 126: 135–146. - PubMed
-
- Buonomo SB, Rabitsch KP, Fuchs J, Gruber S, Sullivan M, et al. (2003) Division of the nucleolus and its release of CDC14 during anaphase of meiosis I depends on separase, SPO12, and SLK19. Dev Cell 4: 727–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

