Prognostic Role of Mucin Antigen MUC4 for Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27305093
- PMCID: PMC4909222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157878
Prognostic Role of Mucin Antigen MUC4 for Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Prognostic Role of Mucin Antigen MUC4 for Cholangiocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 28;18(4):e0285348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285348. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37115797 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and objective: Surgery carries the best hope for cure in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma (CC), whereas surgical outcome is not fully satisfactory. Bio-molecular markers have been used to improve tumor staging and prognosis prediction. Mucin antigen MUC4 (MUC4) has been implicated as a marker for poor survival in various tumors. However, prognostic significance of MUC4 for patients with CC remains undefined. The aim of the present meta-analysis was to investigate the association between MUC4 expression and overall survival (OS) of patients with resected CC.
Methods: The meta-analysis was conducted in adherence to the MOOSE guidelines. PubMed, Embase databases, Cochrane Library and the Chinese SinoMed were systematically searched to identify eligible studies from the initiation of the databases to April, 2016. OSs were pooled by using hazard ratio (HR) with corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI). Random effect models were utilized because of the between-study heterogeneities.
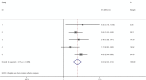
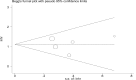
Results: Five studies reporting on 249 patients were analyzed: 94 (37.75%) were in positive or high expression group and 155 (62.25%) in negative or low expression group. The pooled HR for positive or high expression group was found to be 3.04 (95% CI 2.25-4.12) when compared with negative or low expression group with slight between-study heterogeneities (I2 3.10%, P = 0.39). The result indicated that a positive or high expression level of MUC4 was significantly related to poor survival in patients with resected CC. A commensurate result was identified by sensitivity analysis. The main limitations of the present meta-analysis were the rather small size of the studies included and relatively narrow geographical distribution of population.
Conclusion: The result of this meta-analysis indicated that a positive or high expression level of MUC4 was significantly related to poor survival in patients with resected CC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Nakeeb A, Tran KQ, Black MJ, Erickson BA, Ritch PS, Quebbeman EJ, et al. Improved survival in resected biliary malignancies. Surgery. 2002; 132: 555–563; discission 563–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

