Revealing the combined effects of lactulose and probiotic enterococci on the swine faecal microbiota using 454 pyrosequencing
- PMID: 27305897
- PMCID: PMC4919990
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.12370
Revealing the combined effects of lactulose and probiotic enterococci on the swine faecal microbiota using 454 pyrosequencing
Abstract
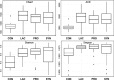
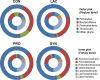
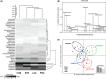
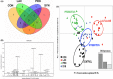
Demand for the development of non-antibiotic growth promoters in animal production has increased in recent years. This report compared the faecal microbiota of weaned piglets under the administration of a basal diet (CON) or that containing prebiotic lactulose (LAC), probiotic Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 11181 (PRO) or their synbiotic combination (SYN). At the phylum level, the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio increased in the treatment groups compared with the CON group, and the lowest proportion of Proteobacteria was observed in the LAC group. At the family level, Enterobacteriaceae decreased in all treatments; more than a 10-fold reduction was observed in the LAC (0.99%) group compared with the CON group. At the genus level, the highest Oscillibacter proportion was detected in PRO, the highest Clostridium in LAC and the highest Lactobacillus in SYN; the abundance of Escherichia was lowest in the LAC group. Clustering in the discriminant analysis of principal components revealed distinct separation of the feeding groups (CON, LAC, PRO and SYN), showing different microbial compositions according to different feed additives or their combination. These results suggest that individual materials and their combination have unique actions and independent mechanisms for changes in the distal gut microbiota.
© 2016 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Bomba, L. , Minuti, A. , Moisá, S.J. , Trevisi, E. , Eufemi, E. , Lizier, M. , et al (2014) Gut response induced by weaning in piglet features marked changes in immune and inflammatory response. Funct Integr Genomics 14: 657–671. - PubMed
-
- Chae, J.P. , Pajarillo, E.A.B. , Park, C.‐S. , and Kang, D.‐K. (2015) Lactulose increases bacterial diveresity and modulates the swine faecal microbiota as revealed by 454‐pyrosequencing. Anim Feed Sci Tech 209: 157–166.
-
- Cho, J.H. , and Kim, I.H. (2013) Effects of lactulose supplementation on performance, blood profiles, excreta microbial shedding of Lactobacillus and Escherichia coli, relative organ weight and excreta noxious contents in broilers. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 98: 424–430. - PubMed
-
- Chun, J. , Lee, J.H. , Jung, Y. , Kim, M. , Kim, S. , Kim, B.K. , and Lim, Y.W. (2007) EzTaxon: a web‐based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57: 2259–2261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

